Recombinant Mouse Tubulin alpha-1A chain (Tuba1a)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Tuba1a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):025306MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:Tuba1a; Tuba1; Tubulin alpha-1A chain; Alpha-tubulin 1; Alpha-tubulin isotype M-alpha-1; Tubulin alpha-1 chain) [Cleaved into: Detyrosinated tubulin alpha-1A chain]
-
免疫原種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
應(yīng)用說(shuō)明:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Here the authors demonstrate that mice lacking the alpha-tubulin acetyltransferase Atat1 in sensory neurons display profound deficits in their ability to detect mechanical stimuli. PMID: 27976998
- Collectively, these findings suggest that Smo and primary cilia-dependent noncanonical Hh signaling leads to post-translational regulation of microtubules and may be important for modulating cell behaviors. PMID: 27793670
- Further PS treatment resulted in recovery of axonal outgrowth and enhanced retrograde axonal transport by decreasing histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) levels and thus increasing acetylation of alpha-tubulin levels. Thus, we have identified the molecular pathway that leads to neurodegeneration in FD and have demonstrated that phosphatidylserine treatment has the potential to slow progression of neurodegeneration PMID: 27997532
- mass spectrometry-based quantitative comparison of acetylated peptides from wild-type vs HDAC6 knockout mice allowed to identify six new deacetylation sites possibly mediated by HDAC6. PMID: 26581825
- These results give new insights into the functions of Tuba1a, mechanisms for regulating tubulin proteostasis, and how compromising these may lead to neural defects. PMID: 26658218
- Data indicate that alpha 1a tubulin (Tuba1a) showed the least variability in expression among the different stages of lung development. PMID: 25723738
- Tubulin-tyrosine ligase (TTL) is required to increase the levels of tyrosinated alpha-tubulin at the axon injury site and plays an important role in injury signaling. PMID: 25911101
- Data suggest a mechanistic link between tubulin hyperacetylation and autophagy induction. PMID: 25404307
- TFIIB co-localizes and interacts with alpha-tubulin during oocyte meiosis in the mouse and depletion of TFIIB causes arrest of subsequent embryo development. PMID: 24244602
- Acetylation of alpha-tubulin is under the control of the acetyltransferase MEC-17 and deacetylases SIRT2 (Sirtuin 2) and HDAC6 (histone deacetylase 6). Adipocyte development is inhibited in MEC-17-knockdown cells, but enhanced in MEC-17-overexpressing cells. PMID: 23126280
- Unambiguous identification of novel glutamylation sites E441 and E443 in mouse brain Tuba1a and Tuba1b. PMID: 22296162
- This study demonistrated that novel tubal(aspartic acid to glycine) mutant mouse is a novel animal model for neurodevelopmental disorders. PMID: 22101068
- These results demonstrate a role for CCP1 in the processing of Glu residues from beta- as well as alpha-tubulin in vitro and in vivo. PMID: 22170066
- Our results highlight the importance of Tuba1a for correct neuronal migration PMID: 21875651
- association between dysferlin and alpha-tubulin, as well as between dysferlin and microtubules PMID: 20405035
- mice harbouring an S140G mutation in Tuba1a present with normal neurogenic potential, but that this neurogenesis is often ectopic PMID: 21041996
- Data indicated that CacyBP/SIP could simultaneously interact with tubulin and actin, suggesting that CacyBP/SIP might link actin and tubulin cytoskeletons. PMID: 20637809
- Data support a model in which stathmin functions in interphase to control the partitioning of tubulins between dimer and polymer pools by setting the number of microtubules per cell. PMID: 19515833
- Mutations in alpha-tubulin in mice and humans that affect neuronal migration result in abnormal lamination of brain structures with associated behavioral deficits. PMID: 17218254
- Loss of alpha-tubulin polyglutamylation in ROSA22 mice is associated with abnormal targeting of KIF1A and modulated synaptic function. PMID: 17360631
- The results uncover alpha-tubulin as a target of the Elongator complex and suggest that a tight regulation of its acetylation underlies the maturation of cortical projection neurons. PMID: 19185337
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton.
-
蛋白家族:Tubulin family
-
組織特異性:Ubiquitously expressed, although primarily in lung and brain.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
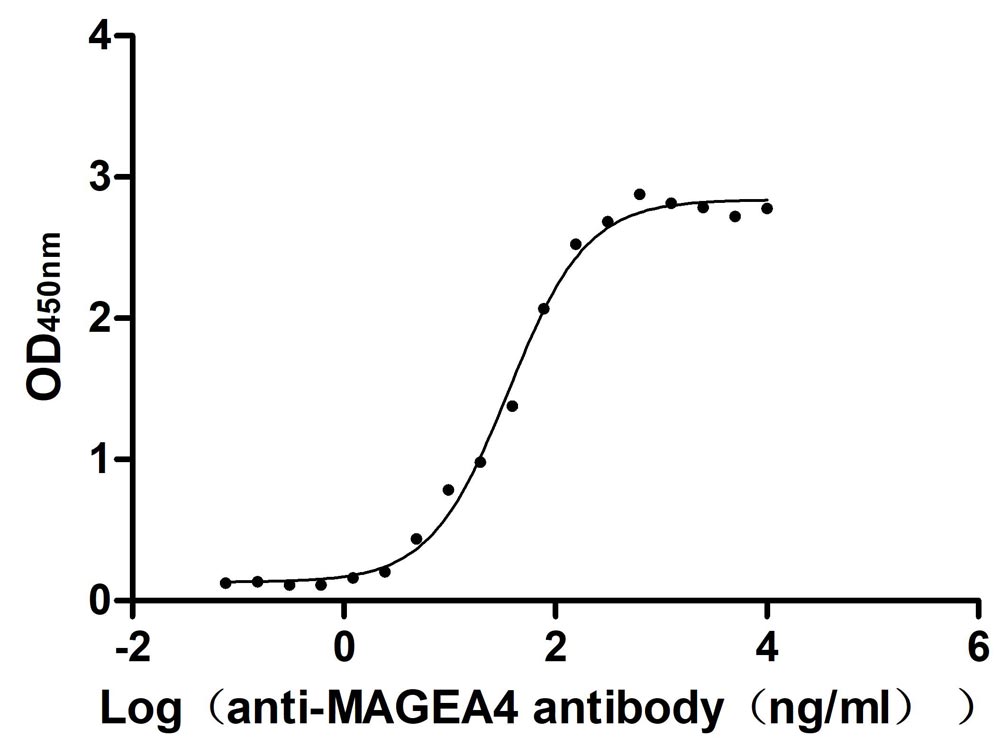
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
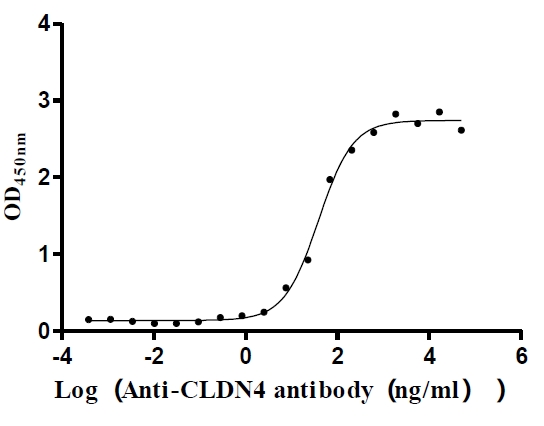
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
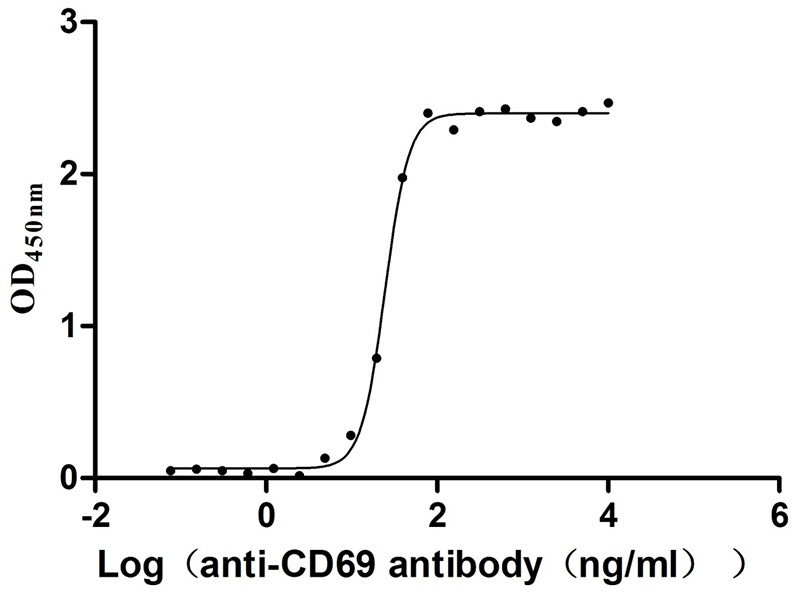
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
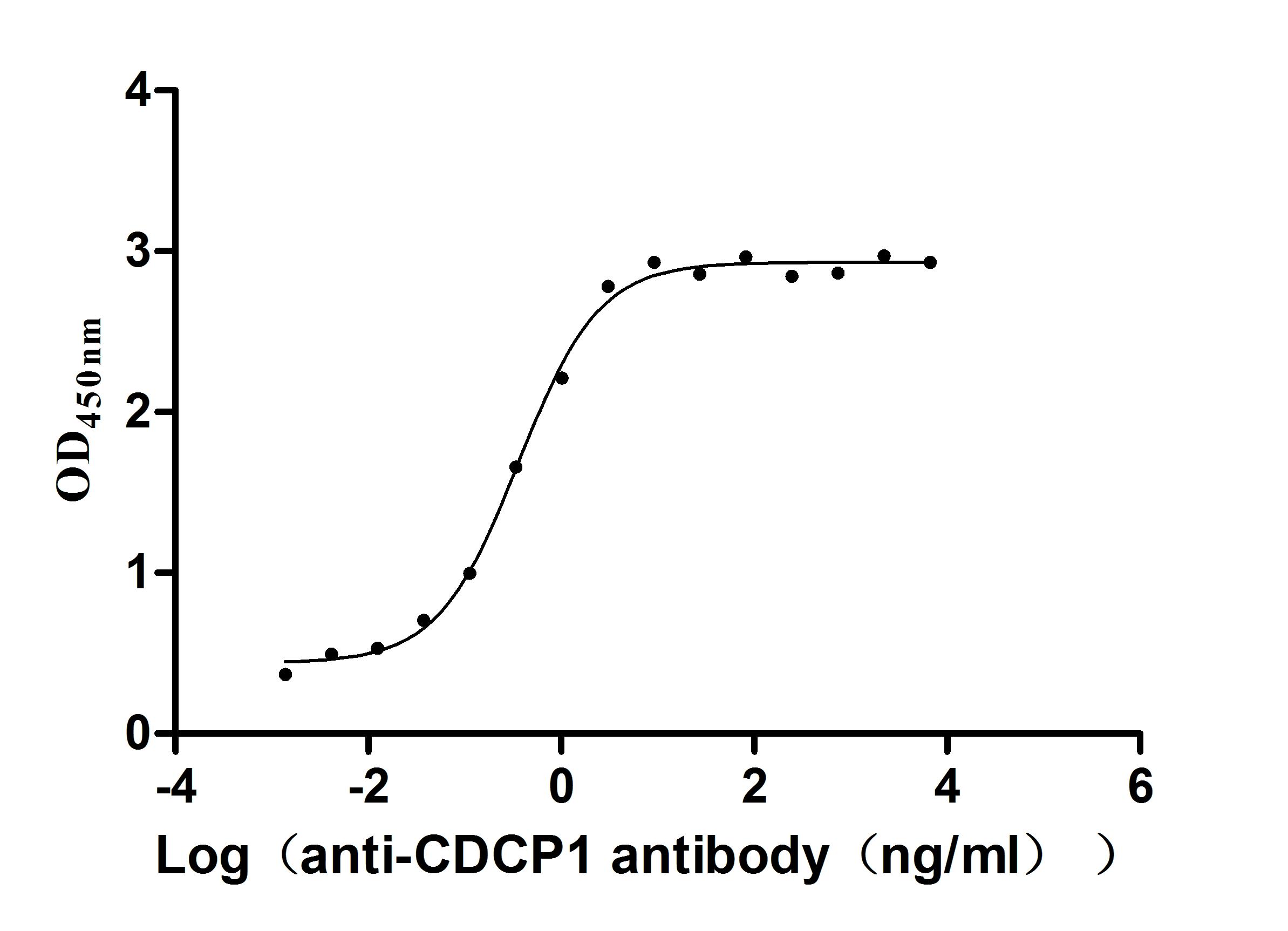
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
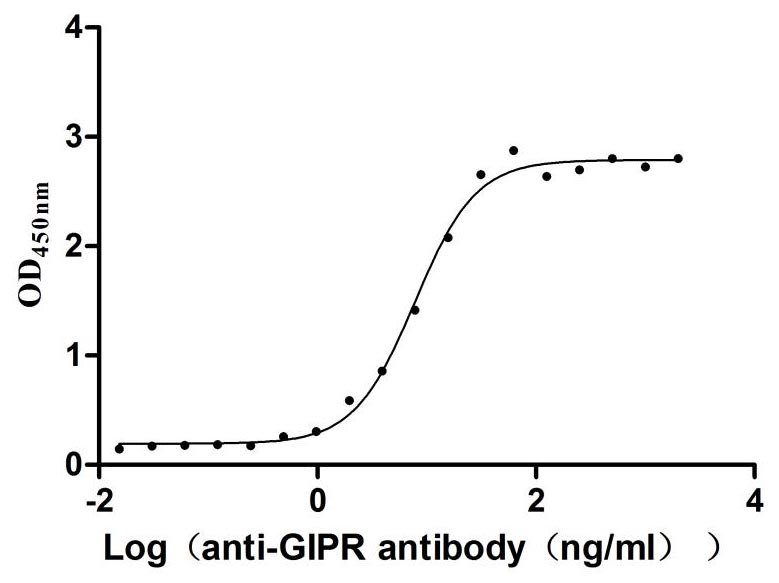
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
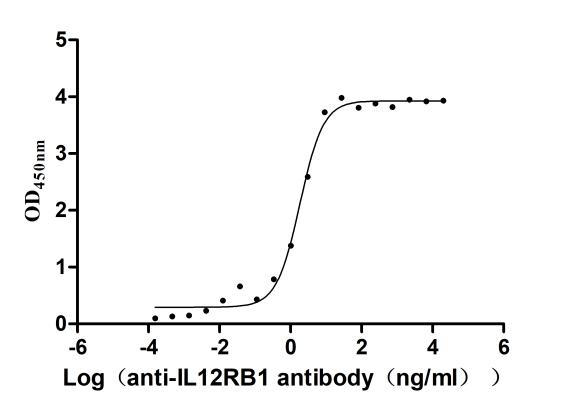
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)