Recombinant Drosophila melanogaster Epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr), partial
-
中文名稱:黑腹果蠅Egfr重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP007479DLU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:黑腹果蠅Egfr重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP007479DLU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:黑腹果蠅Egfr重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP007479DLU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:黑腹果蠅Egfr重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP007479DLU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:黑腹果蠅Egfr重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP007479DLU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Egfr; c-erbB; DER; top; CG10079; Epidermal growth factor receptor; Egfr; EC 2.7.10.1; Drosophila relative of ERBB; Gurken receptor; Protein torpedo
-
種屬:Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Receptor tyrosine kinase, binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses. Known ligands include spitz, gurken, vein and giant-lens. Transduces the signal through the ras-raf-MAPK pathway. Critical for the proliferation of imaginal tissues, and for the determination of both the antero-posterior and dorso-ventral polarities of the oocyte. In the embryo, plays a role in the establishment of ventral cell fates, maintenance of amnioserosa and ventral neuroectodermal cells, germ band retraction, cell fate specification in the central nervous system, and production and repair of the cuticle. During dorsal closure (DC) functions with the dpp- and ACK-signaling pathways to regulate expression of the myosin zip in the embryonic epidermis and amnioserosa (AS), and thus coordinate the progression of epidermal cell shape changes required for correct DC. In the embryonic epidermis, functions by negatively regulating dpp and consequently the dpp-dependent expression of the myosin zip. In the AS, negatively regulates the production/ and or secretion of a diffusible signal which, is produced by the ACK-signaling pathway, and acts in the AS and epidermal cells to promote zip expression. Also required in the AS to inhibit or delay apoptosis, and consequently slow the rate of DC. Therefore functions at multiple levels to negatively regulate morphogenesis during DC, suggesting that it acts as a general brake mechanism for adjusting the rate of dorsal closure to ensure that closure proceeds smoothly and without loss of epidermal integrity. During oogenesis, one of two tyrosine kinase chemoattractant receptors (Egfr and Pvr), that function in the border cells (BC) to detect guidance cues from the oocyte and transduce this information to the guidance pathway that regulate the collective migration of the BC cluster through the nurse cells to the oocyte.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- stress-dependent EGFR/MAPK promotes gut regeneration via a novel mechanism that operates independently of Insulin/Pi3K/TOR signaling. PMID: 28485389
- Data show that EGFR controls the proper formation of brain neuroblasts by regulating the number, survival and proneural gene expression of neuroectodermal progenitor cells which suggest that EGFR signalling is crucially important for patterning and early neurogenesis of the brain. PMID: 27974623
- The activity of Gro is antagonized by EGFR signaling, which inhibits Gro-dependent repression via p-ERK mediated phosphorylation. PMID: 27836963
- we find that EGFR regulates the apical determinant Crb and the extracellular matrix regulator Serp, two factors previously known to control tube length. EGFR regulates the organisation of endosomes in which Crb and Serp proteins are loaded PMID: 28678789
- Avermectin directly interacts with EGFR and leads to the activation of the EGFR/AKT/ERK pathway. PMID: 27249340
- The dorsoventral patterning and EGFR signaling genes play essential roles in correct identity determination and differentiation of lateral glia in the Drosophila nervous system. PMID: 26318336
- Our findings provide in vivo evidence for the role of adult neurons in the maintenance of glia and a novel role for EGFR signaling in the autophagic flux. PMID: 25909451
- Gro inhibits rho expression in undifferentiated cells and represses the expression of both ato and rho in non-R8 precursors during initiation of photoreceptor differentiation in an E(spl)-dependent manner. PMID: 26417727
- strategy for producing ordered square cell packing configurations in epithelia and reveal a molecular mechanism by which organized tissue structure is generated through spatiotemporally regulated responses to EGF receptor activation. PMID: 26506305
- the findings indicate that Vps4 can promote EGFR activity through an endocytosis-independent mechanism. PMID: 25790850
- Drosophila compound eye development is a good model for studying the Egfr signaling pathway. PMID: 25707069
- Mechanistically, miR-998 operates by repressing dCbl, a negative regulator of EGFR signaling. Significantly, dCbl is a critical target of miR-998 since dCbl phenocopies the effects of miR-998 on dE2f1-dependent apoptosis in rbf mutants PMID: 25058496
- FGFR signaling most likely affects ethanol-induced behavior through a different mechanism, possibly through acute action in adult neurons. PMID: 24498174
- Epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) signaling in somatic stromal intermingled cells (ICs), activated by its ligand produced in germ cells, controls the size of the primoridal germ cell pool at the onset of gametogenesis. PMID: 23376160
- Terminal differentiation is promoted in testes expressing a constitutively active EGF Receptor in Drosophila. PMID: 23940622
- Step acts downstream of the EGFR and is required for the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and the induction of EGFR target genes PMID: 23549788
- this study demonistrated that the EGFR signaling in the brain is necessary for olfactory learning in Drosophila larvae PMID: 23512935
- Drosophila Hox and sex-determination genes control segment elimination through EGFR and extramacrochetae activity. PMID: 22912593
- The EGFR pathway acts through bantam to control tissue growth. PMID: 22445297
- Evidence suggests that Pum functions as a negative regulator of EGFR signaling by directly targeting components of the pathway in Drosophila. PMID: 22514614
- Findings provide strong evidence that Msk signals non-autonomously through the Vein-Egfr signaling pathway for late tendon cell late differentiation and/or maintenance. PMID: 21925492
- Egfr signaling is required for specification of alternative neuroblast identities. PMID: 21653613
- EGFR/Ras/MAPK signaling mediates adult midgut epithelial homeostasis and regeneration in Drosophila PMID: 21167805
- EGFR pathway coordinates stem cell proliferation and gut remodeling following infection. PMID: 21176204
- EGFR activation is regulated by transient expression of Rhomboid (Rho), which is required for the maturation of the EGF ligand Spitz. PMID: 20724446
- survival of a subset of midline glia cells depends upon direct suppression of the proapoptotic protein HID via the EGF receptor/RAS/MAPK pathway PMID: 11832242
- EGFR signaling is necessary and sufficient to activate apterous (ap) expression, thereby segregating the wing disc into compartments PMID: 11880345
- mediates cell communication in Drosophila oogenesis PMID: 12015287
- calcineurin, upon activation by Ca(2+)-calmodulin, cooperates with other factors to negatively regulate Egf receptor signaling at the level of sprouty and the GTPase-activating protein Gap1 PMID: 12019233
- role of EGFR-Ras signaling in leg patterning PMID: 12114628
- EGFR signaling plays a role in morphogenesis by modulating cell adhesion PMID: 12163402
- limb development in flies: the distal region is actually patterned by a distal-to-proximal gradient of RTK activity, established by a source of epidermal growth factor (EGF)-related ligands at the presumptive tip PMID: 12181568
- Bristles induce bracts via the EGFR pathway on Drosophila legs. PMID: 12204262
- Pointed and Tramtrack69 establish an EGFR-dependent transcriptional switch to regulate mitosis PMID: 12447387
- Removing the function of EGFR results in aberrant proliferation and reduced size in the brain lateral to the foregut. PMID: 12646129
- Data show that Kekkon-1 can interact with mammalian ErbB receptors and that the Kek1/epidermal growth factor receptor interaction inhibits growth factor binding, receptor autophosphorylation and Erk1/2 activation in response to EGF. PMID: 12900463
- These results indicate that EGFR signaling is crucial for dve expression in the ventral ectoderm and is required in the middle midgut where it cooperates with Dpp signaling. PMID: 14592438
- EGFR and wingless signaling pathways interact to specify the ocellar pattern in Drosophila PMID: 14656001
- Suppression of Wg and Egfr activities is an early step in the development of the peripodial epithelium of the wing discs.uppression of Wg and Egfr activities is an early step in the development of the peripodial epithelium of the wing discs. PMID: 14660540
- Activity of Vein ligand is controlled both positively and negatively, demonstrating the existence of additional levels at which Egfr signaling can be regulated. PMID: 15238521
- EGFR has a role in recruiting ectodermal attachment cells during the organogenesis of Drosophila proprioceptors PMID: 15296720
- Argos inhibits DER signalling without interacting directly with the receptor, but instead by sequestering the DER-activating ligand Spitz PMID: 15329724
- EGF receptor signaling has a role in regulating pulses of cell delamination from the Drosophila ectoderm PMID: 15572130
- Interactions between Notch, Egfr,and dpp protein signaling pathways regulate vein differentiation during pupal wing development. PMID: 15704120
- A genome-wide analysis of transcript levels after perturbation of the Egfr pathway in the ovary was used to identify potential Egfr targets in oogenesis. PMID: 15704171
- contribution of several polymorphisms in the Epidermal growth factor receptor (Egfr) gene to wing shape and size, that were previously mapped in populations of Drosophila melanogaster from North Carolina (NC) and California (CA). PMID: 16102176
- aveugle is required between ras and raf for EGFR signaling in the eye PMID: 16600911
- Activity of crossveinless-c, a gene coding for a RhoGAP and whose specific transcriptional activation in the tracheal cells is triggered by both the trachealess patterning gene and the EGF Receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway. PMID: 16818611
- D-CblS and D-CblL may downregulate Egfr through distinct mechanisms PMID: 16844358
- Dystroglycan links EGFR-induced repression of the anterior follicle cell fate and anterior-posterior polarity formation in the oocyte PMID: 16908845
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, Tyr protein kinase family, EGF receptor subfamily
-
組織特異性:Ubiquitously expressed in embryos. In larvae, uniform expression is seen in wing disks, genital disk, anlagen of testis and ovary, and brain cortex. In eye-antenna disk, highest expression is anterior to morphogenetic furrow, levels remain high in photore
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
KEGG: dme:Dmel_CG10079
STRING: 7227.FBpp0071571
Most popular with customers
-
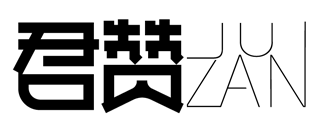
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
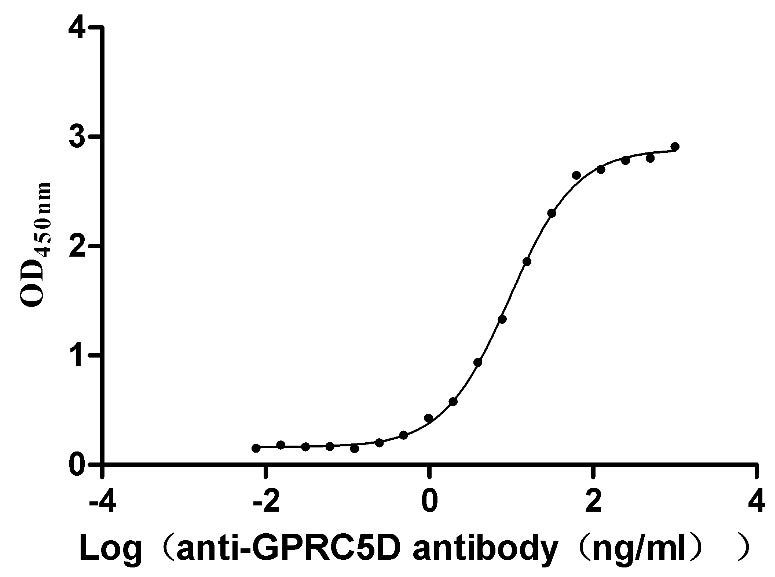
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
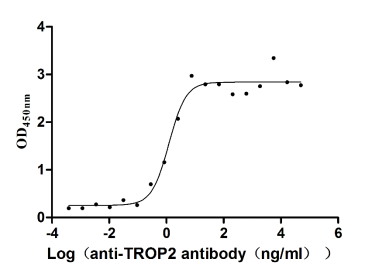
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
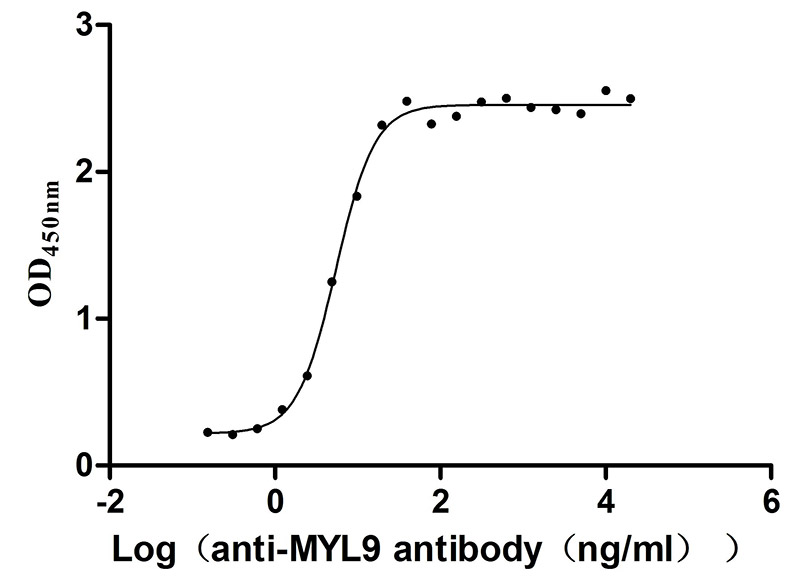
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
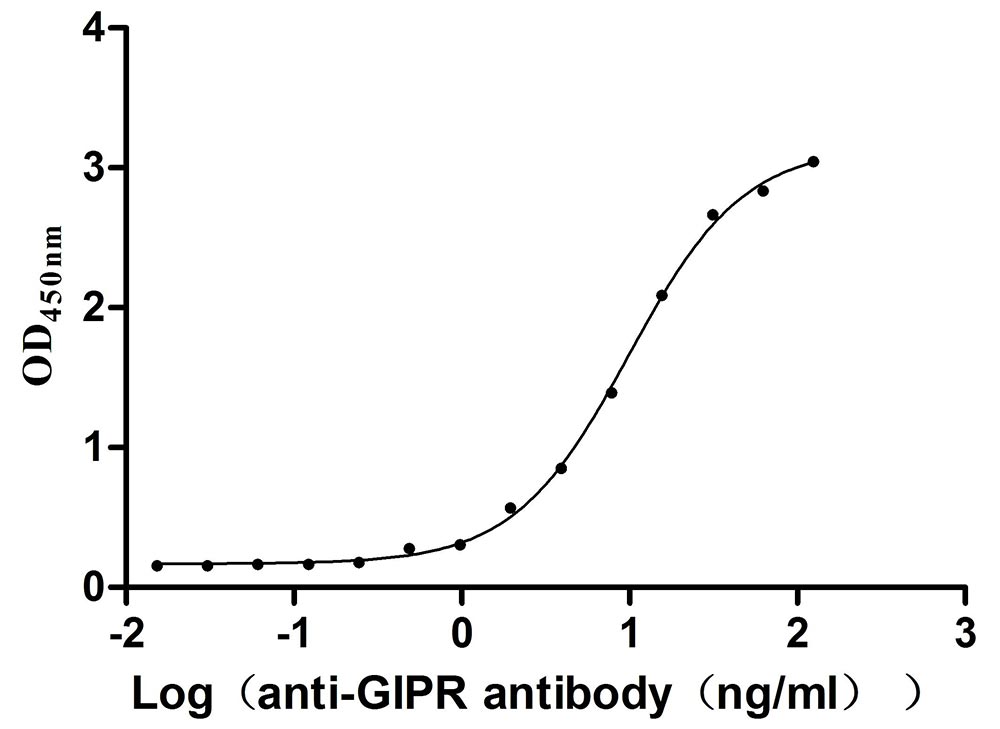
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
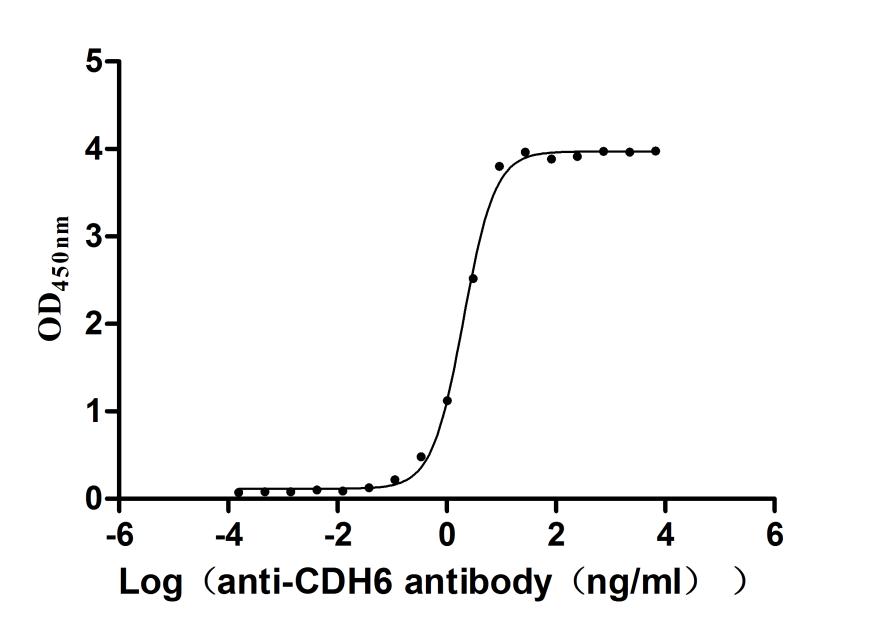
Recombinant Mouse Cadherin-6(Cdh6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)

-AC1.jpg)