Recombinant Human DNA fragmentation factor subunit beta (DFFB)
In Stock-
中文名稱:人DFFB重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP006738HU
-
規(guī)格:¥1836
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
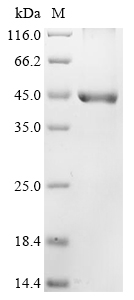
純度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full Length
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
分子量:45.1 kDa
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:1-338aa
-
氨基酸序列MLQKPKSVKLRALRSPRKFGVAGRSCQEVLRKGCLRFQLPERGSRLCLYEDGTELTEDYFPSVPDNAELVLLTLGQAWQGYVSDIRRFLSAFHEPQVGLIQAAQQLLCDEQAPQRQRLLADLLHNVSQNIAAETRAEDPPWFEGLESRFQSKSGYLRYSCESRIRSYLREVSSYPSTVGAEAQEEFLRVLGSMCQRLRSMQYNGSYFDRGAKGGSRLCTPEGWFSCQGPFDMDSCLSRHSINPYSNRESRILFSTWNLDHIIEKKRTIIPTLVEAIKEQDGREVDWEYFYGLLFTSENLKLVHIVCHKKTTHKLNCDPSRIYKPQTRLKRKQPVRKRQ
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
蛋白標(biāo)簽:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose.
-
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:3-7 business days
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
問(wèn)答及客戶評(píng)論
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Nuclease that induces DNA fragmentation and chromatin condensation during apoptosis. Degrades naked DNA and induces apoptotic morphology.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- we show that executioner caspase activation of the apoptotic nuclease CAD/DFF40 is essential for TRAIL-induced mutations in surviving cells. As exposure to chemotherapy drugs also activates apoptotic caspases and presumably CAD, we hypothesized that these pathways may also contribute to the mutagenesis induced by conventional chemotherapy drugs, perhaps augmenting the mutations that arise from direct DNA damage PMID: 28981092
- Dff40 expression is upregulated in atherosclerotic plaque. PMID: 28007744
- the low expression levels of DFF40/CAD and the absence of DNA laddering as common molecular traits in glioblastoma PMID: 26755073
- Data suggest DFF40 expression in breast cancer cell line is involved in drug sensitivity/resistance to doxorubicin; apoptotic cell death due to doxorubicin (a topoisomerase II inhibitor) is enhanced by DFF40 overexpression in breast cancer cell line. PMID: 26529233
- Combinatorial use of some sulfonamides such as acetazolamide along with increased expression of DFF40 can potently kill tumor cells via apoptosis. PMID: 25086620
- DFF40/CAD-independent mechanism driving conformational nuclear changes during caspase-dependent cell death PMID: 24838313
- the highest order of chromatin compaction observed in the later steps of caspase-dependent apoptosis relies on DFF40/CAD-mediated DNA damage by generating 3'-OH ends in single-strand rather than double-strand DNA nicks/breaks PMID: 23430749
- These results suggest a cooperative activity between CAD and DNAS1L3 to accomplish internucleosomal DNA fragmentation . PMID: 23229555
- Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 protein inhibits DNA fragmentation via interaction with DNA fragmentation factor 40 PMID: 22609799
- During apoptotic rearrangement of interchromatin granule clusters, the nuclear matrix (NuMa rearrangement) and chromatin are closely associated. This process occurs in defined stages and depends on the activity of protein phosphatases, caspases and CAD. PMID: 22023725
- the cytosolic levels of DFF40/CAD are determinants in achieving a complete apoptotic phenotype, including oligonucleosomal DNA degradation. PMID: 22253444
- Data show that among the 13 SNPs in the 3 genes, only 3 were found to be polymorphic: R196K and K277R in the DFFB gene, and S12L in the EndoG gene, and all 6 SNPs in the FEN-1 gene were entirely monoallelic. PMID: 22011247
- These data suggest that DFF 40 mediated apoptosis plays a significant role in mediating sepsis induced cellular dysfunction. PMID: 21820410
- Mutations and aberrantly spliced transcripts for the CAD gene are frequently associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 12610505
- Hsp70 binds free CAD in TCR-stimulated T cells to stabilize and augment its activity. PMID: 12738667
- CAD involves unrestricted accessibility of chromosomal DNA at the initial phase of apoptosis, followed by its nuclear immobilization that may prevent the release of the active nuclease into the extracellular environment. PMID: 15569712
- PARP-1 poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is a terminal event in the apoptotic response that occurs in response to DNA fragmentation and directly influences DFF40 activity PMID: 15703174
- Interactions identified here between human placenta histone H1 carboxyl-terminal domain and DFF40/CAD target and activate linker DNA cleavage during the terminal stages of apoptosis. PMID: 15910001
- Our findings of high frequency of Alu-mediated hCAD deletion in human hepatoma underscore the implication of hCAD in hepatocarcinogenesis PMID: 16007181
- AIF is responsible for stage I nuclear morphology and HMW DNA degradation is a caspase-activated DNase and AIF-independent process PMID: 16049016
- levels of CAD were significantly higher in the nuclear fraction of temporal lobe epilepsy samples PMID: 16121124
- DFFB haploinsufficiency from 1p allelic loss is a contributing factor in oligodendroglioma development PMID: 16156899
- in apoptotic cells, endogenous and exogenous CAD forms limited oligomers, representing the active nuclease PMID: 16204257
- the N-terminal region was found to be responsible for the requirement of salt for fibril formation PMID: 16428311
- CAD is downregulated at the mRNA and protein level during the erythroid differentiation in TF-1 cells. PMID: 16529748
- poly-glutamic acid and heparin inhibit DFF40/CAD, the latter one being highly effective at nanomolar concentrations. The inhibitory poly-anions bind to the nuclease and impair its ability to bind double-stranded DNA. PMID: 16699957
- These results suggest that CAD is the endogenous endonuclease that mediates internucleosomal DNA degradation in rotenone-induced apoptosis. PMID: 17239993
- Data suggest that erythroblast chromatin degradation may involve caspase activated DNase and apoptosis inducing factor, enzymes distinct from those active in apoptotic cells. PMID: 17492772
- changes induced in DNA conformation upon HMG-box binding makes the substrate more accessible to cleavage by DFF40/CAD nuclease and thus may contribute to preferential linker DNA cleavage during apoptosis PMID: 18239742
- We have found that neither single-stranded DNA, single-stranded RNA, double-stranded RNA nor RNA-DNA heteroduplexes are cleaved by the DFF40/CAD nuclease. PMID: 18283539
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Mouse Claudin-18.2 (Cldn18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
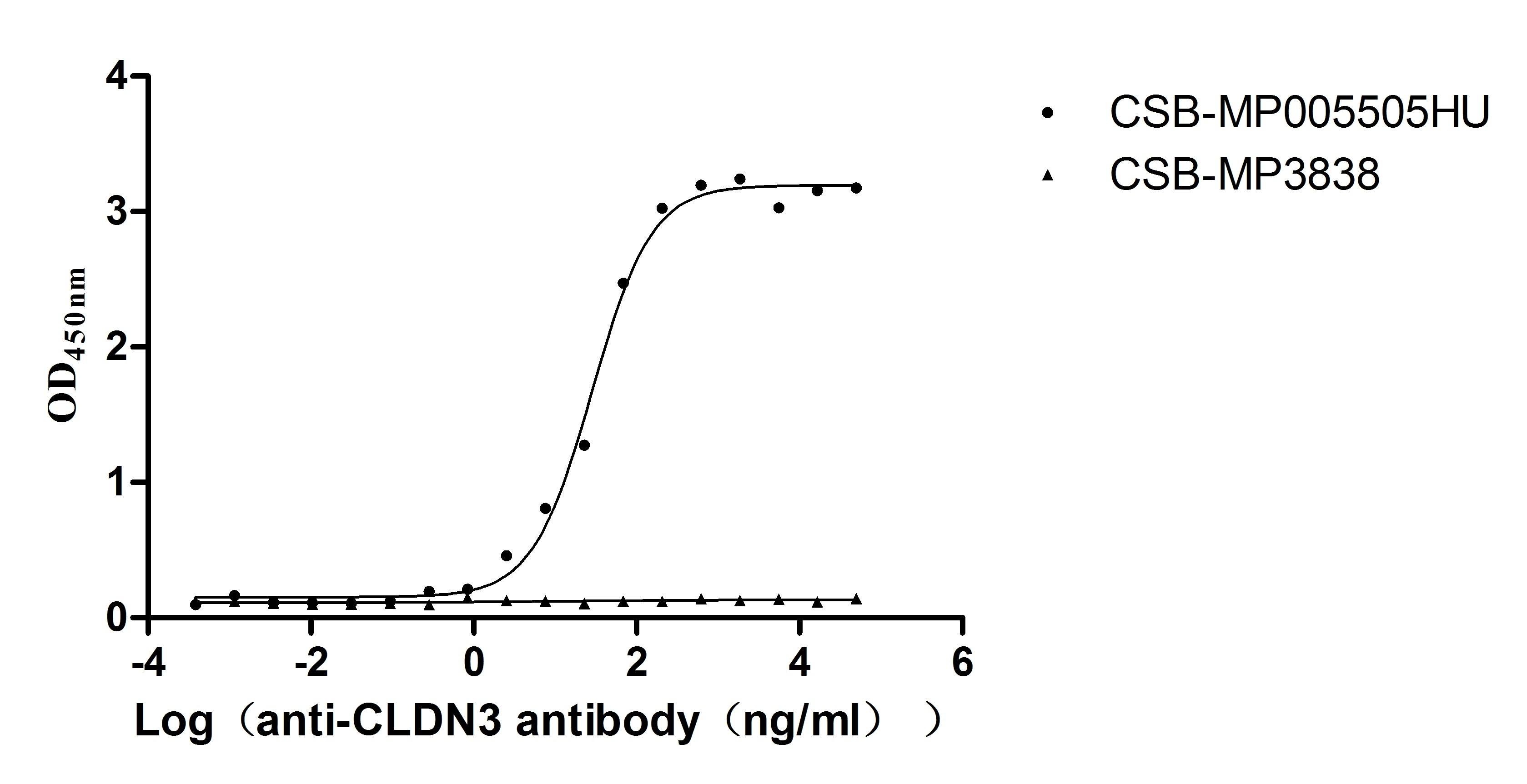
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
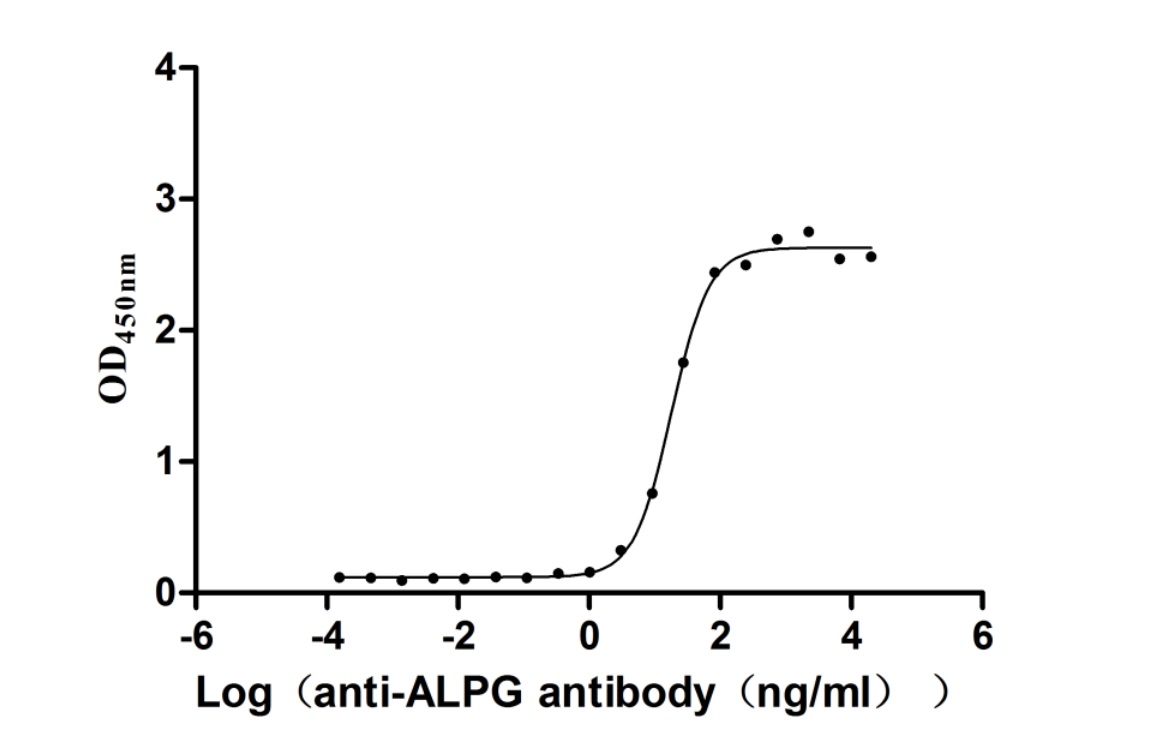
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
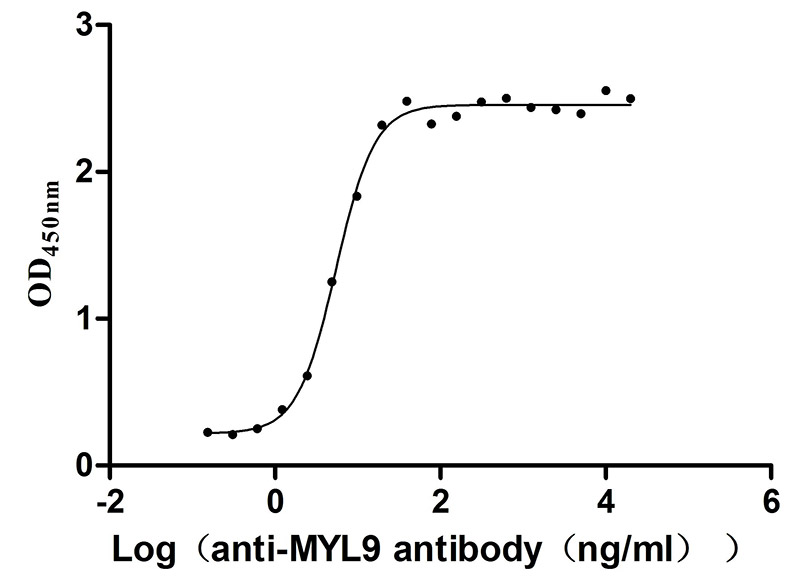
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-type lectin domain family 4 member C (CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)