Recombinant Mouse LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 (Lmo4)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Lmo4重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP013011MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Lmo4重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP013011MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Lmo4重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP013011MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Lmo4重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP013011MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Lmo4重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP013011MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Lmo4
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Lmo4; LIM domain transcription factor LMO4; Breast tumor autoantigen; LIM domain only protein 4; LMO-4
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full length protein
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:1-165
-
氨基酸序列MVNPGSSSQP PPVTAGSLSW KRCAGCGGKI ADRFLLYAMD SYWHSRCLKC SCCQAQLGDI GTSCYTKSGM ILCRNDYIRL FGNSGACSAC GQSIPASELV MRAQGNVYHL KCFTCSTCRN RLVPGDRFHY INGSLFCEHD RPTALINGHL NSLQSNPLLP DQKVC
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Probable transcriptional factor.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Multiple roles of Lmo4 during retinal development. PMID: 26579872
- These results reveal a novel, LMO4-dependent transcriptional program within the basolateral amygdala that is essential to cue-reward learning. PMID: 26134647
- activation of SLK by haptotactic signals requires its recruitment to the leading edge by LMO4 in a Src-dependent manner. PMID: 25882817
- Thus, our study reveals an essential requirement for LMO4 to modulate central insulin signaling. PMID: 24937445
- A novel sensory competent region in the lateral cochlear duct is regulated by LMO4. PMID: 25057208
- By increasing neuronal activity in the paraventricular hypothalamus, food intake was suppressed in LMO4-deficient mice. PMID: 24381275
- LMO4 is a novel modulator of adipogenesis. PMID: 23892074
- The results of this study found that LIM domain only 4 (LMO4) inhibits PTP1B activity by increasing the oxidized inactive form of PTP1B in hypothalamus of mice. PMID: 23904601
- results identify Lmo4 as a central developmental control over the diversity of motor cortex projection neuron subpopulations, establishing their area-specific identity and specialized connectivity. PMID: 23575831
- LMO4 modulates the activity of the DEAF NES, causing nuclear accumulation of a construct containing the LMO4-interaction region of DEAF1. PMID: 22723967
- a selective role for LMO4 in the basolateral complex in modulating learned but not unlearned fear PMID: 22509321
- This study demonitratd that LMO4 as a key regulator of calcium-induced calcium release in central neurons, providing a mechanism for LMO4 to modulate a wide range of neuronal functions and behavior. PMID: 22442089
- LMO4 is expressed in the ventromedial hypothalamic nuclei but not in the arcurate nucleus, and consistent with their predominant effects in regulating fate metabolism/energy expenditure and feeding. PMID: 21874351
- LMO4 and estrogen receptor alpha are associated with the Alk promoter by chromatin immunoprecipitation and Alk is an estrogen-responsive gene in the striatum. PMID: 21976498
- Results indicate that LMO4 promotes the acquisition of cortical neuronal identities by forming a complex with NGN2 and subsequently activating NGN2-dependent gene expression. PMID: 21652654
- Our finding of an essential postnatal function of LMO4 in the differentiation of Bhlhb5-expressing inhibitory interneurons in the retina may be a general mechanism whereby LMO4 controls the production of inhibitory interneurons in the nervous system PMID: 20949055
- Data indicated that there is a genetic interaction between Cited2 and Lmo4 in control of thymus development. PMID: 20549734
- The LMO4 enhances GCSF-induced Stat3 signaling in neurons, in part by sequestering histone deacetylase. PMID: 19997957
- Lmo4 controls the development of the dorsolateral otocyst into semicircular canals and cristae through two distinct mechanisms. PMID: 19913004
- Expression of Lmo4 in a fusion protein in mammary epithelial cells inhibits mammary gland development in mice. PMID: 14676840
- Results suggest that all four members of the LIM-only family -- LMO1, 2, 3, and 4 -- are important regulators of distinct developmental pathways. PMID: 14966285
- Data indicate an important role for LMO4 and Deaf-1 in pathways affecting neural tube closure and skeletal patterning, most likely reflecting their presence in a functional complex in vivo. PMID: 14966286
- LMO4 is essential for proliferation and survival of neural epithelial cells in the rostral neural tube. LMO4 is also expressed in Schwann cell progenitors after these contact neurites, a process mediated in part by neuregulin (Nrg). PMID: 15691703
- the expression profile of Lmo4 suggests that this cofactor is an important regulator of epithelial proliferation PMID: 15805422
- Lmo4 acts as a positive regulator of alveolar epithelial proliferation PMID: 15856027
- LMO4 was confined to the dental epithelium and had spatial temporal expression patterns during tooth morphogenesis. PMID: 16255927
- These observations identify LMO4 as a calcium-dependent transactivator that plays a key role in patterning thalamocortical connections during development. PMID: 16899735
- These findings indicate that the Get-1 and LMO4 genes interact functionally to regulate epidermal terminal differentiation. PMID: 16949565
- Thus, our results suggest that ATP modulates recruitment of RNA-binding proteins to the 3'UTR to stabilize LMO4 mRNA. PMID: 17418808
- Data reveal that LMO4 is a rapidly induced downstream effector of ATP signaling that promotes neuron survival from hypoxia. PMID: 17524392
- Study demonstrates that the LIM-only domain protein, LMO4 serves as a functional partner of GRHL3 in its established roles, and define a new cooperative role for these factors in another developmental epidermal migration event, eyelid fusion. PMID: 18619436
- LMO4 plays essential roles in directing a balanced generation of inhibitory and excitatory neurons in the ventral spinal cord. PMID: 19323994
- The LIM-homeodomain-related genes Lmo4 and Clim1 are initially expressed by both CPN and subcerebral PN in layer V, and only during mid to late differentiation does expression of Lmo4 and Clim1 become largely segregated into distinct neuronal subtypes. PMID: 19366868
顯示更多
收起更多
-
組織特異性:Expressed in a wide variety of tissues.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
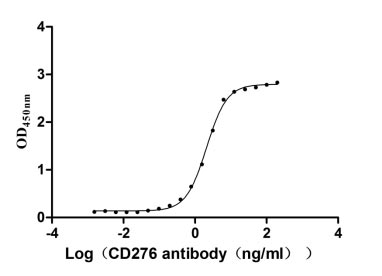
Recombinant Human CD276 antigen (CD276), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
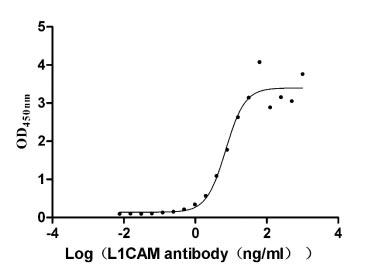
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
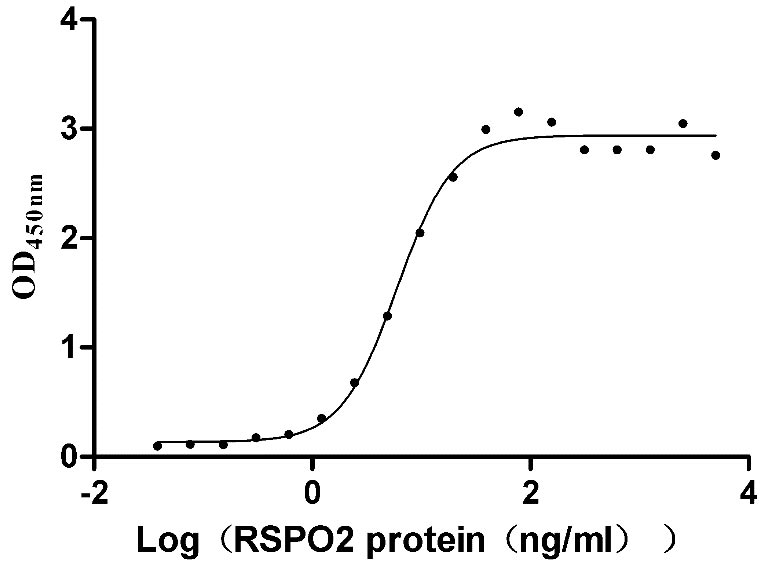
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 (ZNRF3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
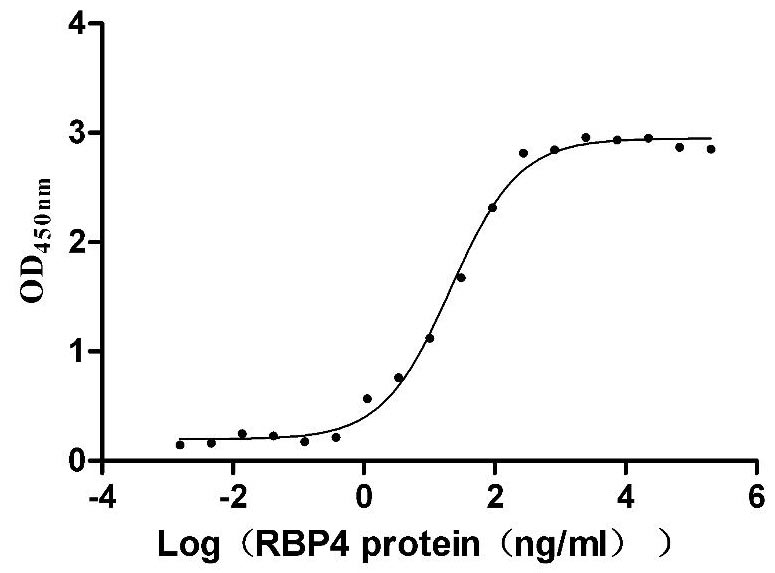
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
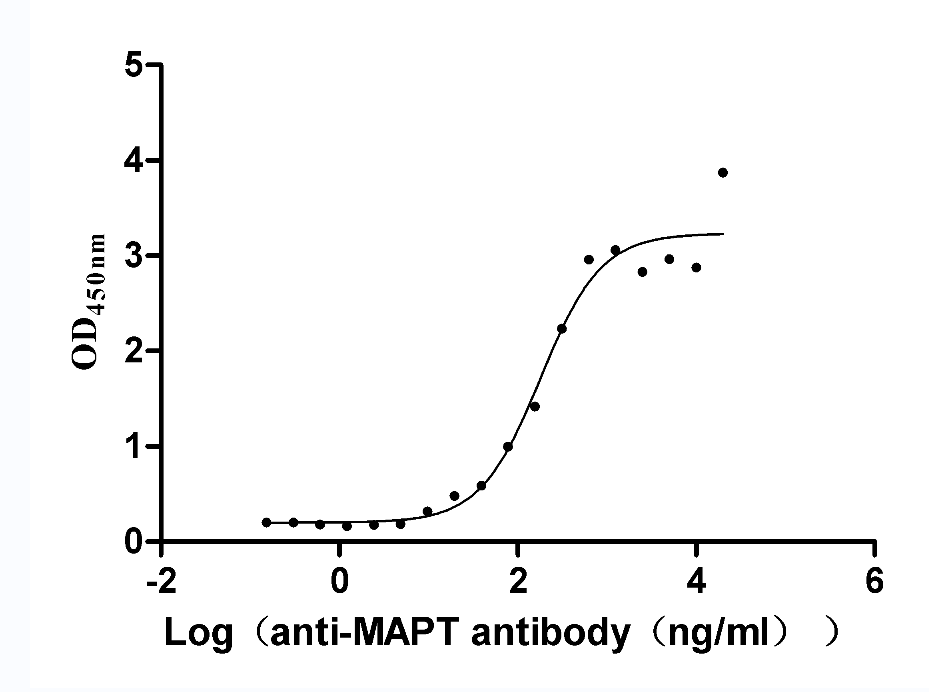
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
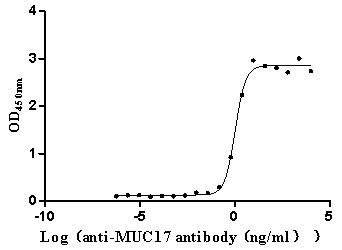
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
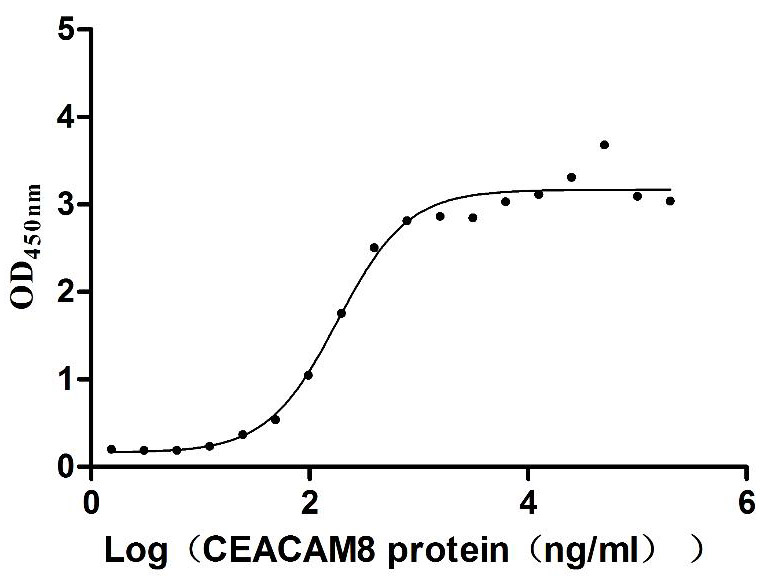
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)