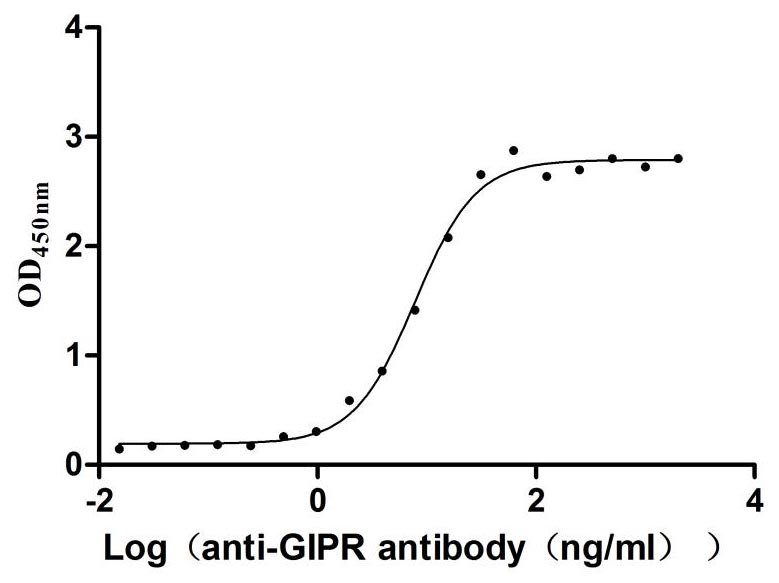
Recombinant Mouse Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5 (Nfat5), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Nfat5重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP893896MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Nfat5重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP893896MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Nfat5重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP893896MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Nfat5重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP893896MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Nfat5重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP893896MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Nfat5Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; NF-AT5; Rel domain-containing transcription factor NFAT5; T-cell transcription factor NFAT5
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Transcription factor involved in the transcriptional regulation of osmoprotective and inflammatory genes. Regulates hypertonicity-induced cellular accumulation of osmolytes.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- TonEBP suppresses M2 phenotype via downregulation of the IL-10 in M1 macrophages. PMID: 27160066
- Here the authors report a lipopolysaccharide-induced NFkappaB enhanceosome in which TonEBP is required for the recruitment of p300. Increased expression of TonEBP enhances the NFkappaB activity and reduced TonEBP expression lowers it. PMID: 27118681
- Data suggest that protease 2A of CVB3 exhibits substrate specificity that includes human/mouse Nfat5 in cardiomyocytes; Nfat5 inhibits CVB3 replication via mechanism that involves iNOS; anti-CVB3 activity of Nfat5 is impaired during CVB3 infection due to protease 2A-mediated cleavage of Nfat5. (CVB3 = Coxsackievirus 3; Nfat5 = tonicity-responsive nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; iNOS = nitric oxide synthase type II) PMID: 29220410
- predominant role in promoting proinflammatory macrophage functions PMID: 29150563
- NFAT5 can modulate different T-cell responses depending on stress conditions and stimulatory context. PMID: 27479742
- results provide evidence that NFAT5 expression in macrophages enhances chronic arthritis by conferring apoptotic resistance to activated macrophages. PMID: 28192374
- In vivo, osmotic stress up-regulates the SCTR gene in the kidney cortex and medulla of wild-type mice, but does not do so in NFAT5(+/-) mice. PMID: 27080132
- TonEBP suppresses adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity by blocking epigenetic transition of PPARgamma2 PMID: 26042523
- TonEBP is a critical regulator of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier leakage in kainic acid-induced seizures. PMID: 24608792
- role in sodium-induced increase in monocytic cell adhesion PMID: 24573382
- PKC-alpha contributes to high NaCl-dependent activation of NFAT5 through ERK1/2. PMID: 25391900
- Suggest that biomechanical stretch is sufficient to activate NFAT5 both in native and cultured VSMCs where it regulates the expression of tenascin-C. PMID: 24614757
- Together, these results clearly demonstrated that hyperglycemia-induced TonEBP plays a crucial role in increasing aldose reductase and PKCdelta levels and leading to apoptotic death. PMID: 24631337
- Data indicate that in transgenic mice overexpressing Sfmbt2 10th intron-hosted miR-466a-3p, significant down-regulation of Nfat5 and many other osmoregulation-related genes was observed in both the renal cortex and medulla. PMID: 24389345
- NFAT5 is part of a protective mechanism that limits renal damage induced by IRI. PMID: 24379188
- NFAT5 induction by the pre-T-cell receptor serves as a selective survival signal in T-lymphocyte development. PMID: 24043824
- A novel context-dependent suppression of NFAT5 target gene expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or a high salt (NaCl) concentration, was identified. PMID: 23867654
- NFAT5 is necessary for the transcriptional regulation of AQP4 expression and for local astrocyte swelling with accompanying restriction of the neuropil extracellular space in vivo. PMID: 23180003
- phosphorylated TAZ physically interacted with nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 (NFAT5), a major osmoregulatory transcription factor, and subsequently suppressed DNA binding and transcriptional activity of NFAT5 PMID: 23045390
- These results demonstrated a novel role of NFAT5 in cardiac differentiation of stem cells. PMID: 22935419
- Data indicate that transcriptional coregulator ddx5/ddx17 RNA helicases can simultaneously regulate the transcriptional activity and alternative splicing of NFAT5 transcription factor. PMID: 22266867
- It was concluded that specific DNA binding of NFAT5 contributes to its nuclear localization, by mechanisms as yet undetermined, but independent of ones previously described. PMID: 22992674
- Muscle fibers from type 1 diabetic mice exhibited increased NFAT5 expression and transverse tubule disruptions, but no differences in electrically evoked Ca(2+) transients. PMID: 22966145
- NFAT5 was necessary for effective immunity against Leishmania major, a parasite whose clearance requires TLRs and iNOS expression in macrophages. PMID: 22312110
- [review] TonEBP is required for mouse embryonic development and survival. TonEBP is a master regulator of cellular adaptation to hypertonic stress. PMID: 21998140
- These findings demonstrated an essential role of NFAT5 in cardiac development and Ca(2+) signaling. PMID: 21765887
- Identify NFAT5 as a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation. PMID: 21757659
- NFAT5-dependent CD24 induction contributes to T-cell expansion under hypertonic stress in a mouse model. PMID: 21037089
- TonEBP is necessary for the regulation of AQP1 expression in the inner medulla of the kidney under hypertonic conditions. PMID: 20639513
- The loss of nucleosome(s) was found to be initiated by an OREBP-independent mechanism, but was significantly potentiated in the presence of OREBP. PMID: 20041176
- NFAT5 exclusion from mitotic chromatin resets its nucleo-cytoplasmic distribution in interphase PMID: 19750013
- rottlerin dramatically inhibits tonicity-dependent TonEBP expression and TonE-dependent transcription but, does so through a PKCdelta-independent pathway. PMID: 11880333
- TonEBP functions at all stages of mouse development, as well as in isotonic adult tissues PMID: 11934689
- Data show that NFAT5/TonEBP stimulates transcription of HSP70-2, and is a master regulator of the renal medulla for cellular protection against high osmolality via organic osmolytes and molecular chaperones. PMID: 12138186
- NFAT5 is important for cell growth in vivo and within the context of an isosmotic environment plays a role in optimally coordinating transcriptional programs in response to osmotic stresses to which cells are normally exposed in vivo during cell growth. PMID: 12421923
- description of the complete sequence and primary structure of murine Nfat5, two new spliced isoforms, and the expression of murine Nfat5 in embryonic and adult mouse tissues PMID: 12438710
- NFAT5 is a tonicity-responsive transcription factor required for kidney homeostasis and function; knockout mice show renal atrophy. PMID: 14983020
- Data show that NFAT5/TonEBP is not only essential for normal cell proliferation under hyperosmotic conditions but also necessary for optimal adaptive immunity. PMID: 15247420
- Data indicate that in addition to vasopressin, osmotic response element-binding protein (OREBP/Nfat5) is another essential regulator of the urine concentrating mechanism. PMID: 15347663
- OREBP-mediated accumulation of osmolytes is essential during elongation of the lens fiber cells. PMID: 15774462
- Identification of a noncoding RNA repressor of the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activity. PMID: 16141075
- TonEBP influences AQP2 transcriptional activity at least partially by acting directly on the AQP2 promoter PMID: 16641150
- TonEBP, in turn, drives the expression of aldose reductase and urea transporter-A PMID: 16926446
- myoblast migration and differentiation are coupled and that NFAT5 is a key regulator PMID: 17164296
- NFAT5 not only plays an important role in osmotic stress response pathway in hybridoma cells but also is essential for optimal antibody productivity. PMID: 17310218
- NFAT5 is a sensitive responder to pathologic increases in extracellular tonicity in T lymphocytes. PMID: 18221508
- Nup88 is up-regulated in response to hypertonic stress and acts to retain TonEBP in the nucleus, activating transcription of critical osmoprotective genes. PMID: 18606815
- an increase in intracellular ionic concentration and not cell shrinkage is involved in TonEBP activation PMID: 18842831
- Results of these studies suggest that, in nucleus pulposus cells, osmotic pressure and calcium modulate AQP2 expression through TonEBP and are independent of the calcineurin-NFAT pathway PMID: 19138132
- TonEBP activation by calcium controls {beta}1,3-glucuronosyltransferase-I expression, a key regulator of glycosaminoglycan synthesis in cells of the intervertebral disc PMID: 19147493
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Note=Nuclear distribution increases under hypertonic conditions.
-
組織特異性:Detected in white and brown adipose tissue, muscle, heart, liver and kidney. Expressed in lymphocytes (at protein level).
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
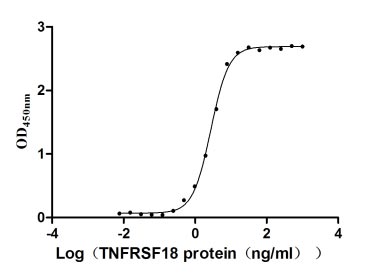
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
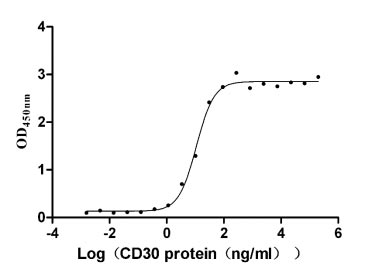
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
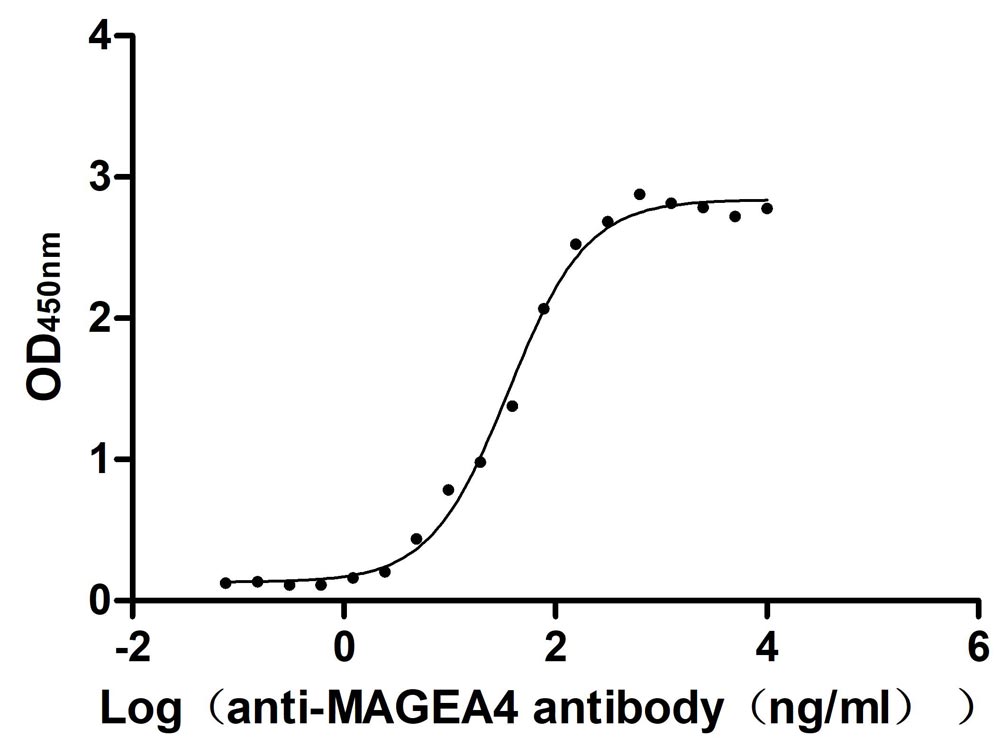
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
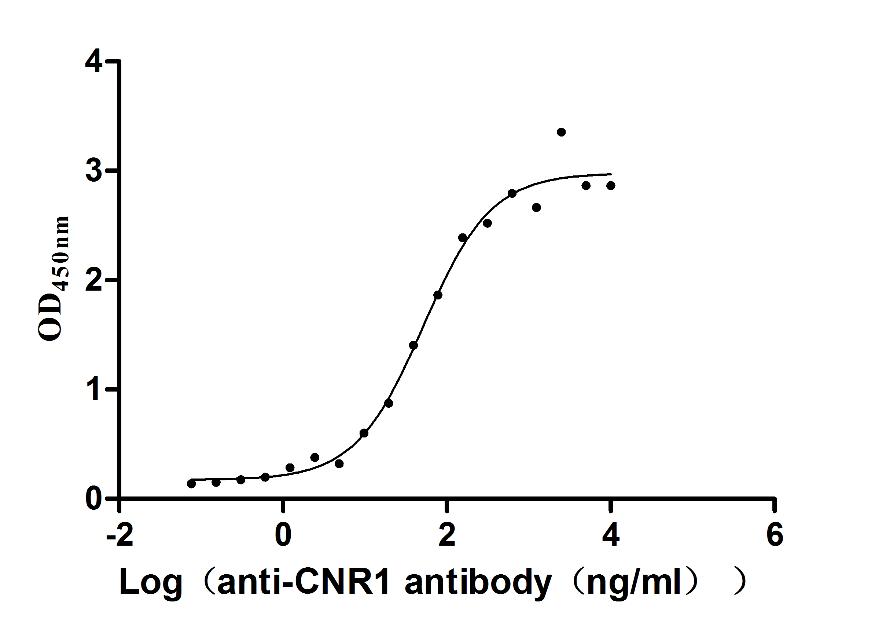
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
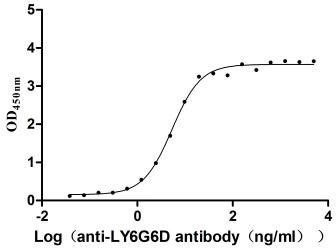
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
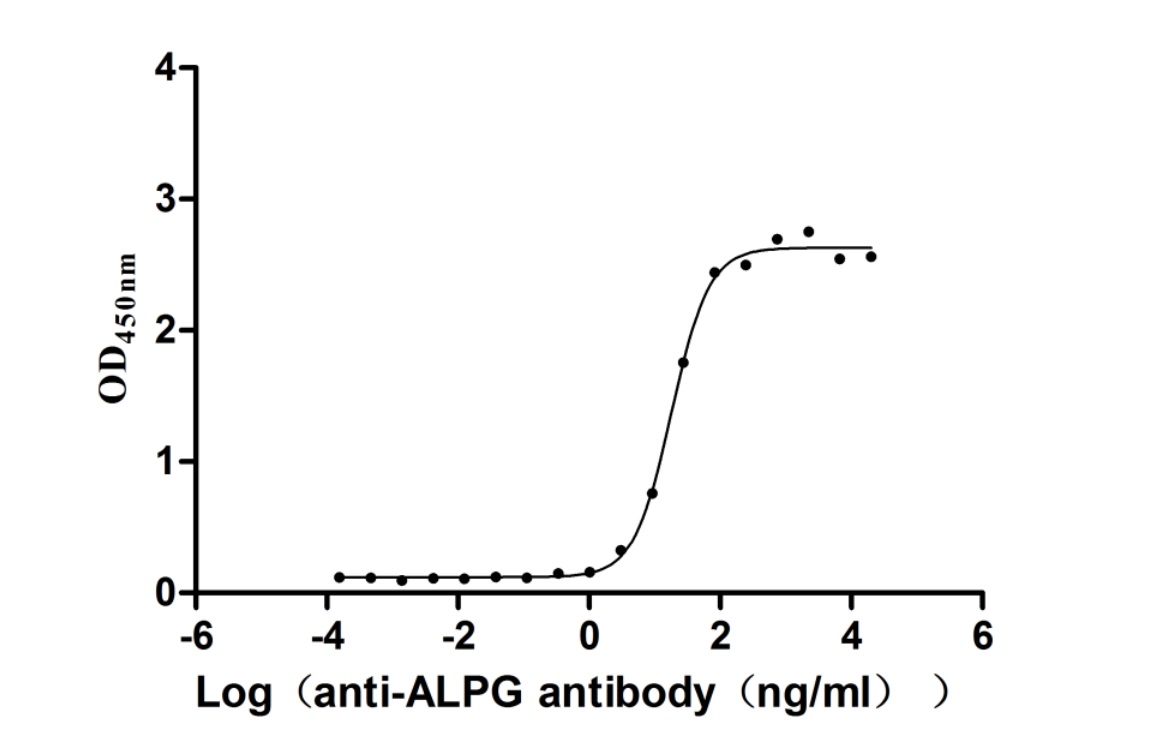
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)