Recombinant Mouse Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3 (Rapgef3), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rapgef3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP844989MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rapgef3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP844989MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rapgef3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP844989MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rapgef3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP844989MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Rapgef3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP844989MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Rapgef3; Epac; Epac1; Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3; Exchange factor directly activated by cAMP 1; Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1; EPAC 1; cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor I; cAMP-GEFI
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RAP1A and RAP2A small GTPases that is activated by binding cAMP. Through simultaneous binding of PDE3B to RAPGEF3 and PIK3R6 is assembled in a signaling complex in which it activates the PI3K gamma complex and which is involved in angiogenesis. Plays a role in the modulation of the cAMP-induced dynamic control of endothelial barrier function through a pathway that is independent on Rho-mediated signaling. Required for the actin rearrangement at cell-cell junctions, such as stress fibers and junctional actin.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- The inactivation of EPAC1 affects the early stage of ebola virus entry. PMID: 30332733
- Epac1 can restore normal insulin signaling in the retinal vasculature through reductions in inflammatory cytokines PMID: 30116147
- Epac activation reduces inflammation and microvascular permeability in an acute lung injury model. PMID: 29174852
- studies indicate that Epac1 plays important roles in promoting VSMC proliferation and phenotypic switch in response to vascular injury, therefore, representing a therapeutic target for vascular proliferative diseases. PMID: 27830723
- These data indicate that Epac1 may be protective to the retina through inhibition of key inflammatory mediators. PMID: 28210097
- Arrhythmic effects of Epac-mediated ryanodine receptor activation in Langendorff-perfused murine hearts PMID: 28316073
- In retinopathy, EPAC-1 expression is decreased in a microRNA-7-mediated manner, contributing to endothelial dysfunction. PMID: 28353063
- Epac1 exerts a tonic inhibition of in vivo basal microvascular permeability PMID: 27096875
- In behavioral tests, Epac1-/- mice exhibited similar phenotype to those of WT mice. PMID: 27598965
- Data suggest that Epac1 reduces formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome to reduce inflammatory responses in the retinal vasculature. PMID: 28348460
- Results demonstrate that Epac1 plays an important role in regulating energy balance and glucose homeostasis by promoting leptin expression and secretion in white adipose tissue. PMID: 27381457
- Epac1 is involved in AC5-mediated catecholamine stress-induced cardiac fibrosis. Epac1 is involved in AC5-mediated elongation of atrial fibrillation. PMID: 27117748
- Within heart mitochondria, different Epac1 microdomains control myocardial cell death. PMID: 28096195
- GRK2 inhibits Epac1-to-Rap1 signaling by phosphorylation of Epac1 at Ser-108 in the Disheveled/Egl-10/pleckstrin domain, inhibiting agonist-induced Epac1 translocation to the plasma membrane, reducing Rap1 activation. PMID: 26929333
- DPP4i restores cardiac remodeling and apoptosis caused by the pathological decline in circulating GLP-1 in response to pressure overload. EPAC1 is essential for cardiomyocyte survival via the cAMP/Rap1 activation independently of PKA. PMID: 26721911
- Epac2, but not Epac1 has a role in decreasing severity of ischemic retinopathy after retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury PMID: 25985753
- Epac1 deficiency attenuates neointima formation through, at least in part, inhibition of SMC migration, in which a decrease in Ca(2+) influx and a suppression of cofilin-mediated lamellipodia formation occur. PMID: 26427796
- PDE4 inhibition reduces neointima formation and inhibits VCAM-1 expression and histone methylation in an Epac-dependent manner. PMID: 25640159
- Epac1 deletion protected against beta-AR-induced cardiac remodelling and prevented the induction of autophagy. PMID: 25411381
- Epac1 induces beta2-AR-mediated masseter muscle hypertrophy without influencing slow-to-fast MHC isoform transition, probably via activation of Akt and its downstream molecules and increase of CaMKII-mediated HDAC4 phosphorylation. PMID: 25344550
- EPAC1 was found to facilitate metastasis of pancreatic ductal carcinoma. PMID: 25385424
- prostacyclin regulates bone growth via the Epac/Rap1 pathway PMID: 25406016
- The results of the present study show that EPAC1 boosts Treg-mediated suppression, and identifies EPAC1 as a target with broad therapeutic potential because Tregs are involved in numerous pathologies PMID: 25339598
- These data identify ICER as a redundant mediator of Treg cells and cAMP action on Teff cells and suggest that Epac may function as an alternative effector to promote cAMP-dependent Teff cell suppression. PMID: 24007532
- Epac1 primarily is capable of inhibiting remodeling processes, whereas Epac2 primarily increases inflammatory processes in vivo PMID: 25103224
- EPAC1 and EPAC2 are critical signaling intermediates in osteoclast differentiation that permit RANKL-stimulated NFkB nuclear translocation and actin rearrangements PMID: 25122553
- Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP is involved in the regulation of adipogenic genes during 3T3-L1 fibroblasts differentiation. PMID: 24444094
- Data suggest that PGE2/Ep4 (prostaglandin E receptor 4; Ptger4) signaling via cAMP/Epac (exchange protein directly activated by cAMP 1; Rapgef3) induces expression of Icam1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) in cerebrovascular endothelial cells. PMID: 23317035
- Epac1 KO exhibited decreased cardiac contractility with reduced phospholamban (PLN) phosphorylation at serine-16, the major PKA-mediated phosphorylation site. PMID: 24892712
- data show the expression EPAC is altered in the cortex, striatum and midbrain of HPRT knockout mouse; propose that the alterations in EPAC/RAP1 signaling and cell migration in HPRT deficiency are crucial for neuro-developmental events that may contribute to neurological dysfunctions in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome PMID: 23804752
- Deletion of Epac1, in mice, protects them from an ordinarily lethal dose of rickettsiae. PMID: 24218580
- The current study provides in vitro and in vivo evidence that Epac1 has an important role in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of beta cells and phenotype resembling metabolic syndrome. PMID: 23825225
- data indicate that the Epac1-Piezo2 axis has a role in the development of mechanical allodynia during neuropathic pain PMID: 23575686
- EPAC interaction with SUR1 controls seizure susceptibility and possibly acts via regulation of glutamate release. PMID: 23678128
- Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 gene ablation attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via CGRP-cAMP/EPAC1 pathway. PMID: 23306833
- TGR5 causes relaxation of gastric smooth muscle and the relaxation is mediated through inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase pathway via both Epac-dependent stimulation of Rap1 and cAMP/PKA-dependent phosphorylation of RhoA PMID: 23275618
- Epac1-deficient mice are more resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity, hyperleptinemia, and glucose intolerance. PMID: 23263987
- This study identifies Epac as the link between cAMP and p38 MAPK signalling pathways and demonstrates that PKCdelta can function as a novel downstream effector of this beta-adrenoceptor/cAMP/Epac pathway PMID: 22103274
- Studying the underlying mechanism revealed a redundant action of the signalling molecules exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP (Epac). PMID: 22050227
- The result od this study suggested that EPAC proteins control miR-124 transcription in the brain for processing spatial learning and social interactions. PMID: 22365550
- analysis of autoinhibition and activation of the exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP (EPAC) and EPAC2 PMID: 21873431
- Epac1 transfection led to cellular hypertrophy and increased protein synthesis, which was accentuated by high glucose ambience which increased the expression of pAkt and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27. PMID: 21854750
- Epac has different roles in regulating cell death in neuronal and myocardial cells PMID: 20516079
- Activation of Epac is necessary but not sufficient for adipogenic conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. PMID: 20036887
- These results led us to conclude that the Epac-Rap-PLC-[Ca2+]i signaling pathway is involved in cAMP-stimulated Cl- secretion, which is carried by a novel, previously undescribed Cl- channel. PMID: 20038525
- Rap1 plays a pivotal role in chemokine-induced integrin activation and migration. Rap1 was activated by secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC; CCL21) and stromal-derived factor 1 (CXCL4) treatment in lymphocytes within seconds. PMID: 12707305
- Epac is present in spermatogenic cells and exhibits a preferential subplasmalemmal localization; data show that cAMP activates Rap1 in differentiating male germ cells which express Epac, suggesting that this activation might occur directly through Epac PMID: 12887090
- possible co-localization of Epac1 and Rap1 proteins in the heads of epididymal spermatozoa PMID: 17077580
- a ternary complex of TCL1, Epac1, and Akt forms in activated macrophages both promoting Akt activation and regulating intracellular distribution of Akt PMID: 17993260
- Epac1 contributes to the hypertrophic effect of beta-adrenergic receptor in a protein kinase A-independent fashion PMID: 18323524
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
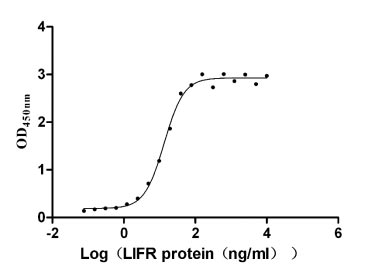
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
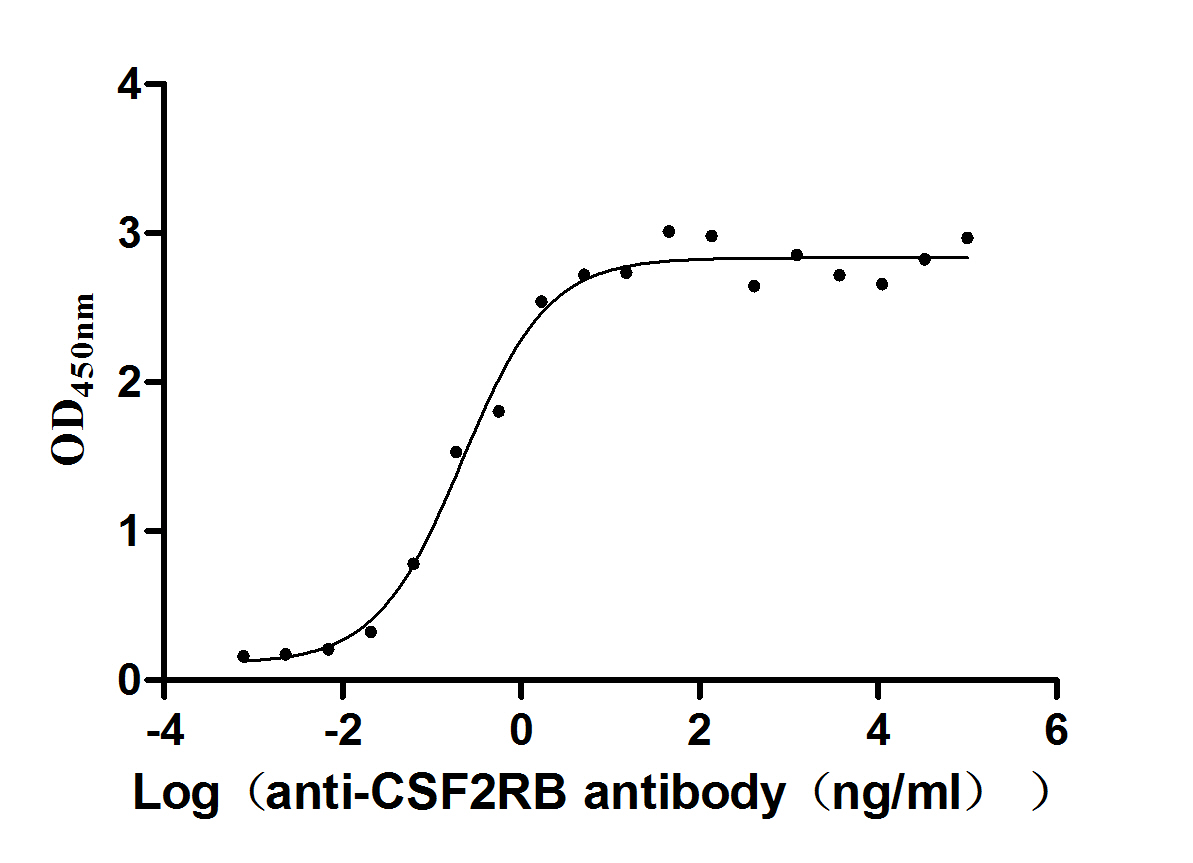
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

-AC1.jpg)