Recombinant Mouse Troponin I, cardiac muscle (Tnni3)
-
中文名稱(chēng):小鼠Tnni3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP341785MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱(chēng):小鼠Tnni3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP341785MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱(chēng):小鼠Tnni3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP341785MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱(chēng):小鼠Tnni3重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP341785MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
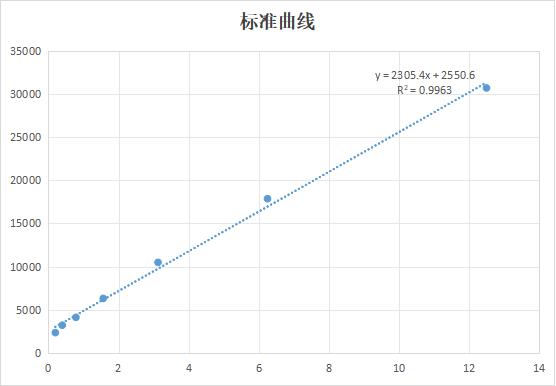
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Tnni3; Troponin I; cardiac muscle; Cardiac troponin I
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:2-211
-
氨基酸序列ADESSDAAG EPQPAPAPVR RRSSANYRAY ATEPHAKKKS KISASRKLQL KTLMLQIAKQ EMEREAEERR GEKGRVLRTR CQPLELDGLG FEELQDLCRQ LHARVDKVDE ERYDVEAKVT KNITEIADLT QKIYDLRGKF KRPTLRRVRI SADAMMQALL GTRAKESLDL RAHLKQVKKE DIEKENREVG DWRKNIDALS GMEGRKKKFE G
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Troponin I is the inhibitory subunit of troponin, the thin filament regulatory complex which confers calcium-sensitivity to striated muscle actomyosin ATPase activity.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Pim-1 is a novel kinase that phosphorylates cTnI primarily at Ser23/24 and Ser150 in cardiomyocytes, which in turn may modulate myofilament function under a variety of physiological and pathophysiological conditions. PMID: 29544221
- Hyperphosphorylation of this serine199 in cTnI C terminus impacts heart function by depressing diastolic function at baseline and limiting systolic reserve under physiological stresses. Paradoxically, it preserves heart function after ischemia/reperfusion injury, potentially by decreasing proteolysis of cTnI. PMID: 28899987
- The contributions of cardiac myosin binding protein C and troponin I phosphorylation to beta-adrenergic enhancement of in vivo cardiac function PMID: 26635197
- The difference in myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation between the ventricles of R21C(+/+) in cardiac troponin I mice likely contributes to observed differences in contractile force and the lower tension monitored in the LV of HCM mice PMID: 25961037
- troponin I phosphorylation specifically alters the Ca(2+) sensitivity of isometric tension and the time course of relaxation in cardiac muscle myofibrils PMID: 25418306
- Combined troponin I Ser-150 and Ser-23/24 phosphorylation sustains thin filament Ca(2+) sensitivity playing an adaptive role to preserve contraction during acidic ischemia. PMID: 24657721
- these results indicate that the inability to enhance myofilament relaxation through cTnI phosphorylation predisposes the heart to abnormal diastolic function, reduced accessibility of cardiac reserves, dysautonomia, and hypertrophy. PMID: 24973218
- Dominant negative TnI-TnT interface mutation decreases the binding affinity of cTnI for TnT, causes early ventricular remodeling, and blunts the beta-adrenergic response of cardiac myocytes. PMID: 24898585
- R193H and R205H mutation increase the binding affinity of Troponin I for Troponin T and Troponin C. PMID: 24326031
- Conclude that dilated cardiomyopathy-causing mutations in thin filament proteins abolish the relationship between myofilament Ca(2+) sensitivity and troponin I phosphorylation by PKA. PMID: 23539503
- The pattern of cTnI post-translational modification depends on sex and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy genotype. PMID: 23352598
- A new functional and pathological role of amino acid modifications in the N-terminal acidic domain of cardiac TnI has been found that is modified by phosphorylations at TnI(S23/S24). PMID: 22940544
- Data show that cardiac TnI gene transition and the alternatively spliced cardiac TnT isoform switching occur in postnatal pulmonary vein. PMID: 23176202
- Conclude that cTnI phosphorylation by AMPK may represent a novel mechanism of regulation of cardiac function. PMID: 22456184
- Generation and functional characterization of knock-in mice harboring the cardiac troponin I-R21C mutation associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PMID: 22086914
- Data suggest that AMPK emerges as a possibly important regulator of cardiac and skeletal contractility via phosphorylation of a preferred site adjacent to the inhibitory loop of the thin filament protein TnI. PMID: 21416543
- Loss of troponin I leads to myofibril hypersensitivity to Ca(2+) causing impaired relaxation in restrictive cardiomyopathy. PMID: 20580639
- the functional effect of cTnI mutation and its potential value in compensating for the cTnT abnormality PMID: 20551314
- Ca(2+) binding to thin filaments reconstituted with either cTnI(wild-type) or pseudo-phosphorylated cTnI(S23D/S24D), cTnI(T144E), and cTnI(S23D/S24D/T144E) was determined. PMID: 20164197
- Studies indicate that that immunization of genetically susceptible mice with troponin I but not troponin T induced a robust autoimmune response leading to marked inflammation and fibrosis in the myocardium. PMID: 19446498
- calcium induces an extended conformation of the inhibitory region of troponin I in cardiac muscle troponin PMID: 11724531
- regulation of myocyte twitch kinetics by beta-stimulation and by endothelin-1 was altered in myocytes containing mutant cTnI PMID: 11934831
- PKC-mediated phosphorylation of Ser(43) and Ser(45) of cTnI plays an important role in regulating force development in the intact myocardium PMID: 12003851
- Troponin I serines 43/45 and regulation of cardiac myofilament function. PMID: 12181153
- demonstration of novel site specificity of effects of protein kinase C phosphorylation on function and emphasize the complexity of modulation of the actin-myosin interaction by specific changes in the thin filament PMID: 12551921
- the relationship between sarcomere length and myofilament lattice spacing in troponin I transgenic mice was markedly shifted downward to an overall decreased myofilament lattice spacing following protein kinase a treatment. PMID: 12562915
- A primary role of PKC phosphorylation of cTnI may be to reduce the requirements of the contractile apparatus for both Ca2+ and ATP, thereby promoting efficient ATP utilisation during contraction. PMID: 12923217
- autoantibodies to cTnI induce heart dysfunction and dilatation by chronic stimulation of Ca2+ influx in cardiomyocytes PMID: 14595408
- PKC-dependent phosphorylation of TnI has important role in the modulation of cardiac function under basal as well as augmented states PMID: 14726296
- cTnI has a pivotal role in the positive inotropic response of the murine heart to beta-adrenergic stimulation. PMID: 14966306
- protein kinase C phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I plays a dominant role in depressing contractility PMID: 15507454
- In conclusion, these data (alpha-chloralose-urethane) demonstrate that alpha-adrenergic-mediated force reduction is mediated through troponin I protein kinase C phosphorylation PMID: 15579573
- removal of the N-terminal extension of cTnI enhances cardiac function by increasing the rate of myocardial relaxation and lowering left ventricular end diastolic pressure to facilitate ventricular filling PMID: 15611140
- phosphorylation is driven by p90RSK PMID: 15840586
- The Ca2+ binding properties of various assemblies of the regulatory components that contain one of the cardiomyopathy-related mutant cTnI. PMID: 16531415
- Abnormal TnI phosphorylation observed in cardiac failure may explain exacerbated relaxation delay in response to increased afterload and contribute to blunted chronotropic reserve. PMID: 16936010
- The cTnI-G203S mutation disrupts interactions with partner proteins, and results in intracellular Ca2+ dysregulation early in life, suggesting a pathogenic role in development of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PMID: 16950368
- TnI deficiency impairs left ventricular relaxation, which leads to diastolic heart failure. PMID: 17526646
- cTnI-Cre mice have delayed onset of Cre activity during early heart development PMID: 17540338
- key role of cTnI in myocyte relaxation PMID: 17615373
- The primary effect of protein kinase A phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I is reduced Ca(2+) sensitivity of force, whereas phosphorylation of cardiac myosin-binding protein C accelerates the kinetics of force development. PMID: 17641226
- Changes in Ca(2+) affinity also support the idea that the equilibrium between states of actin-tropomyosin-troponin was shifted to the inactive state by mutations that mimic troponin I phosphorylation. PMID: 17872964
- Thr144 in cardiac TnI modulates cardiac myofilament length-dependent activation. PMID: 17975107
- Lys184 deletion in troponin I impairs relaxation kinetics and induces hypercontractility in murine cardiac myofibrils. PMID: 18096573
- Simultaneous defects in MHC7 & TnI accelerate onset & progression of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Compared with single-mutant models, double-mutant mice develop severe disease & premature death, progressing directly to a dilated phenotype. PMID: 18362229
- Impaired relaxation is the main manifestation in transgenic mice expressing a restrictive cardiomyopathy mutation, R193H, in cardiac TnI. PMID: 18408133
- Removal of the N-terminal extension of cardiac troponin I as a functional compensation for impaired myocardial beta-adrenergic signaling PMID: 18815135
- Transfer of troponin I-specific T cells can induce inflammation and fibrosis in wild-type mice, leading to deterioration of contractile function. Two sequence motifs of cTnI that induce inflammation and fibrosis in myocardium are characterized. PMID: 18955666
- These results indicate that YY1 is a novel regulator of fetal TnI transcription in the heart. PMID: 19013134
- the nNOS-PMCA4b complex regulates contractility via cAMP and phosphorylation of both PLB and cTnI. PMID: 19278978
顯示更多
收起更多
-
蛋白家族:Troponin I family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
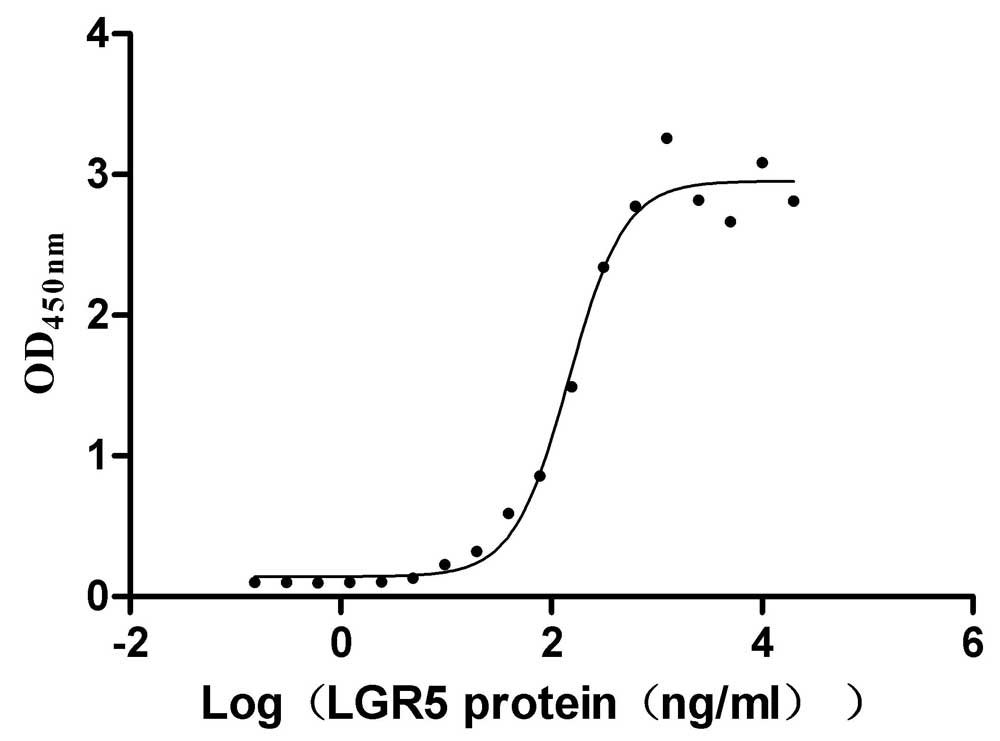
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
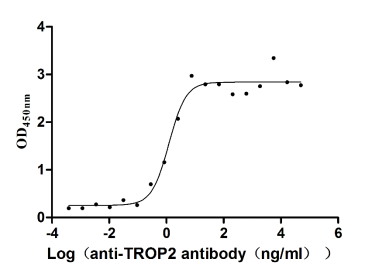
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
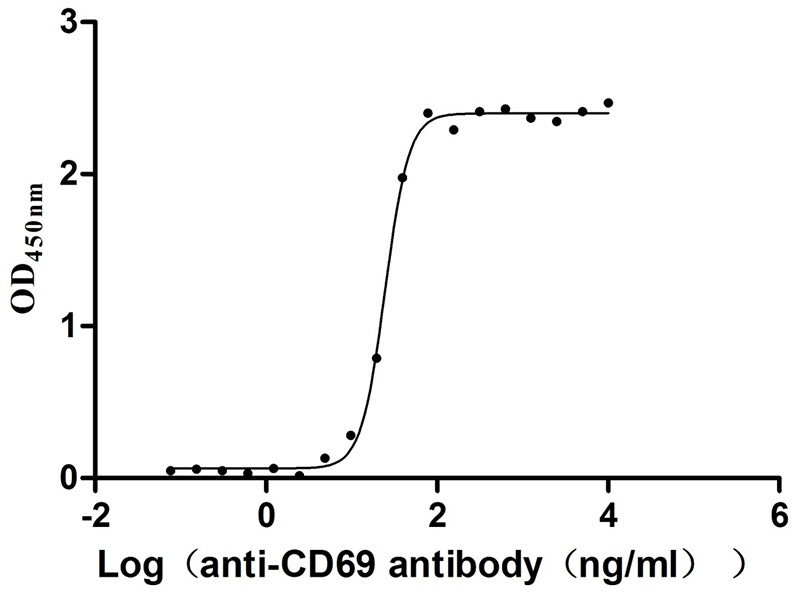
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
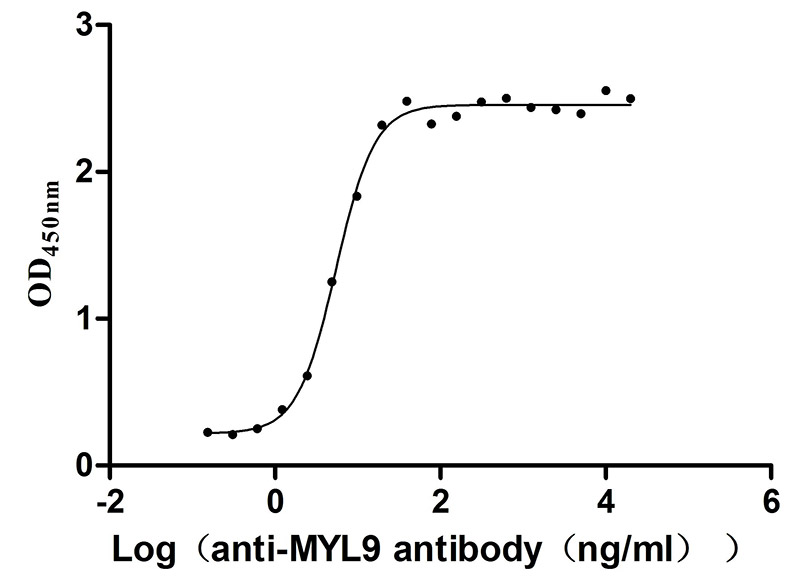
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(PLAU) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

-AC1.jpg)