Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Serine/threonine-protein kinase TOR1 (TOR1), partial
-
中文名稱:釀酒酵母TOR1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP327400SVG
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:釀酒酵母TOR1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP327400SVG
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:釀酒酵母TOR1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP327400SVG-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:釀酒酵母TOR1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP327400SVG
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:釀酒酵母TOR1重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP327400SVG
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:TOR1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:TOR1; DRR1; YJR066W; J1803; Serine/threonine-protein kinase TOR1; EC 2.7.11.1; Dominant rapamycin resistance protein 1; Phosphatidylinositol kinase homolog TOR1; Target of rapamycin kinase 1
-
種屬:Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase homolog, component of TORC1, which regulates multiple cellular processes to control cell growth in response to environmental signals. Nutrient limitation and environmental stress signals cause inactivation of TORC1. Active TORC1 positively controls ribosome biogenesis via control of rRNA, ribosomal protein and tRNA gene expression, and rRNA processing. TORC1 positively controls protein biosynthesis by regulation of mRNA stability, translation initiation factor activity, and high-affinity amino acid permeases that serve to provide amino acids for use by the translation machinery. TORC1 also promotes growth by sequestering a number of nutrient and general stress-responsive transcription factors in the cytoplasm. TORC1 negatively controls macroautophagy, a process to recycle surplus cytoplasmic mass under nutrient starvation conditions. TORC1 controls many of these processes via TIP41-TAP42-mediated inhibition of the type 2A-related phosphatases PP2A and SIT4. In nutrient rich conditions, responsible for the phosphorylation of AGC S6 kinase (S6K) YPK3, activating YPK3 kinase activity and promoting phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Phosphorylates kinase SCH9 at 6 amino acids in the C-terminus, activating SCH9 kinase activity to properly regulate ribosome biogenesis, translation initiation, and entry into stationary phase.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- We also show that Tor1p vacuolar localization and TORC1 anabolic functions, including growth promotion and phosphorylation of its direct substrate Sch9, are compromised in s-hhy mutants. Thus, an intact trans-Golgi and late endosome interface is a requisite for efficient Tor1 vacuolar localization and TORC1 function. PMID: 27812735
- Overexpressing SCH9, but not TOR1, allows newly-formed tetraploids to exhibit evolved phenotypes and knocking out SCH9 diminishes the evolved phenotypes. Furthermore, when cells were challenged with conditions causing ancestral cells to evolve aneuploidy, tetraploidy was maintained in the evolved lines. Our results reveal a determinant role for Sch9 during the early stage of polyploid evolution. PMID: 27812096
- TORC1 can both promote and inhibit gametogenesis. Down-regulation of TORC1 is required to activate IME1. However, complete inactivation of TORC1 inhibits IME1 induction, indicating that an intermediate level of TORC1 signalling is required for entry into sporulation. PMID: 27272508
- These data show that deletion of any of Ras2, Tor1, or Sch9 proteins mimics calorie restriction and is sufficient to increase cell protection from oxydative stress. PMID: 25238629
- This study presents a detailed characterization of the membrane immersion properties of the oxidized and reduced yeast TOR1 FATC domain (2438-2470 = y1fatc). PMID: 24725177
- The TORC1 pathway is involved in neutral lipid homeostasis in yeast. PMID: 25512609
- Results indicate that Tor-Sch9 deficiency extends longevity by switching cells to an alternative metabolic mode, in which acetic acid can be utilized for the storage of stress resistance carbon sources. PMID: 24649827
- Amino acid deprivation inhibits TORC1 through a GTPase-activating protein complex for the Rag family GTPase Gtr1. PMID: 23716719
- Elo2 phosphorylation is induced upon inhibition of TORC1 and requires GSK3. PMID: 24239358
- Characterization of the interactions of the yeast TOR1 FATC domain with membrane mimetic micelles, bicelles, and small unilamellar vesicles. PMID: 24704685
- TOR1 and TOR2 deficiency retard aging and carbonyl/oxidative stress development in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PMID: 24834721
- decreases in the levels of glutathione and its precursors resulting from the introduction of a Tor1 hyper-active mutation PMID: 23832372
- Tor1 and Tor2, are essentially required for proper endocytic protein dynamics at the early stage of endocytosis. PMID: 23660670
- Deltator1 cells showed a mild increase in nuclear Hcm1. PMID: 23481038
- inhibition of nutrient-sensitive target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) stimulates Orm phosphorylation and synthesis of complex sphingolipids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PMID: 23363605
- Data indicate that the accumulation of proteins in an SDS-insoluble state in postmitotic cells represents autophagic cargo preparation process that is regulated by the Tor1 kinase. PMID: 23097491
- gln3 mutations dissociate responses to nitrogen limitation (nitrogen catabolite repression) and rapamycin inhibition of TorC1 PMID: 23223232
- Regulated expression of TOR1 was important in the activation of the PKC1 CWIP in a myo1Delta strain and hence its survival. PMID: 22646158
- ribosome content is regulated dynamically in eukaryotes by TOR through both ribosome synthesis and the cytoplasmic turnover of mature ribosomes. PMID: 22451491
- TORC1 signaling is coupled to heat-induced SGs to protect cells from DNA damage PMID: 22727621
- TORC1 regulates FA metabolism, likely through modulating the peroxisome and beta-oxidation. direct interactions between Snf1 and TORC1 pathways are unlikely under nutrient-limited conditions. PMID: 22068328
- extension of chronological life span by reduced TOR1 complex/Sch9p-mitochondrial signaling occurs independently of Rim15p and is not a function of changes in media acidification/composition PMID: 21641548
- inhibition of target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling and subsequent induction of autophagy promoted an increase in targeting of Rnr1 to the vacuole and a decrease in soluble Rnr1 protein levels. PMID: 21343333
- The longevity-increasing action of the afo1 deletion mutation is independent of mitochondrial translation, yet involves the cytoplasmic Tor1p as well as the growth-controlling transcription factor Sfp1p. PMID: 20157544
- The Sch9p kinase is a key downstream effector of oxidative phosphorylation, reactive oxygen species metabolism and chronological life span in the TOR-mitochondria pathway. PMID: 20157595
- Binding studies with TOR1 fatc domain in which tryptophans were replaced by alanine suggest that these residues are important for exact positioning in the membrane and that the other residues in the lipid-binding motif contribute to the affinity. PMID: 20042596
- Decreased nucleotide excision repair observed following rapamycin treatment is independent of TORC1/2 function and likely due to a function of Fap1. PMID: 19805410
- mediator of glucose repression effect of PRX1 through inhibition of MSN2/4 PMID: 15598536
- TOR1 and PKA regulate Ribosomal protein gene transcription involves the Forkhead-like transcription factor FHL1. PMID: 15620355
- structural data, redox potential of the disulfide bridge, and the biochemical data of a cysteine to serine mutant indicate that intracellular redox potential can affect the cellular amount of the target of rapamycin (TOR)protein via the FATC domain PMID: 15772072
- TOR and PKA coregulate LYS gene expression. PMID: 16397762
- These findings suggest that the association of the Tap42-phosphatase complexes with TORC1 represents an important mechanism by which nutrient controls Tor signaling activity. PMID: 16874307
- results indicate that the spatial regulation of TOR complex 1 (TORC1) might be involved in differential control of its target genes; data indicate that TOR might be more intimately involved in gene regulation than previously thought PMID: 16900101
- interactions between the FRB (rapamycin binding) domain and kinase domains, as well as between the FRB domain and the TORC1 component Kog1p, regulate TOR activity as well as contribute to the mechanism of caffeine resistance PMID: 16923813
- Deletion of the TOR1 gene extends chronological life span in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PMID: 17403371
- These results reveal the broad scope of cellular processes influenced by TORC1, and they underscore the functional overlap between TORC1 and TORC2. PMID: 17507646
- Results support a model whereby TOR1/TORC1 act as a survival pathway in response to genotoxic stress by maintaining the deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools necessary for error-prone translesion DNA polymerases. PMID: 17698581
- Overproduction of non-translatable mRNA may functionally inactivate the nuclear cap-binding complex (CBC), and inactivation of CBC may then hyperstimulate the TORC1 pathway to mediate Ty1 transcriptional silencing. PMID: 18435413
- TOR1 and TOR2 have distinct localization patterns, consistent with the regulation of cellular processes. PMID: 18723607
- These results provide new insight into Sec14 function, and they emphasize the trans-Golgi network/endosomal system as a central hub for homeostatic regulation in eukaryotes. PMID: 18753406
- TOR signaling pathway is specifically involved in the regulation of cell death initiated by telomere dysfunction. PMID: 18949037
- Tor1 and Sch9 are central components of a network that controls a common set of genes implicated in a metabolic switch from the TCA cycle and respiration to glycolysis and glycerol biosynthesis. PMID: 19424415
- Npr2/3 complex mediates an amino acid starvation signal to TORC1. PMID: 19521502
- YPK1 overexpression resulted salt stress hypersensitivity and this hypersensitivity was dependent on TOR1. PMID: 19835169
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Vacuole membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side.
-
蛋白家族:PI3/PI4-kinase family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
KEGG: sce:YJR066W
STRING: 4932.YJR066W
Most popular with customers
-
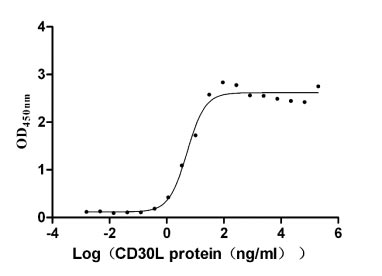
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
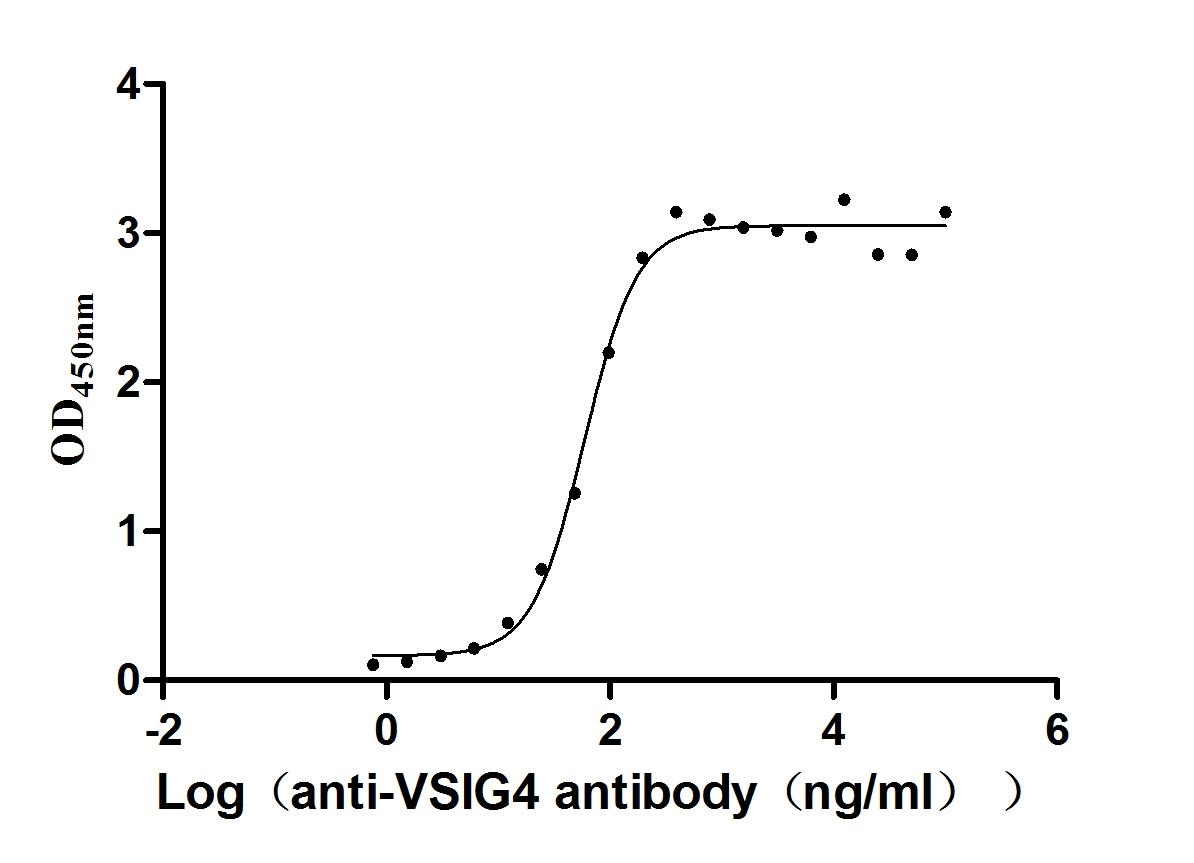
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
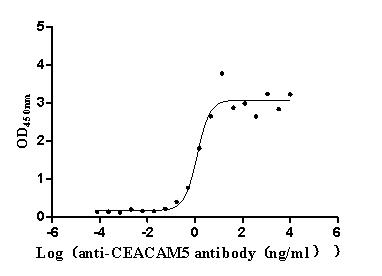
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
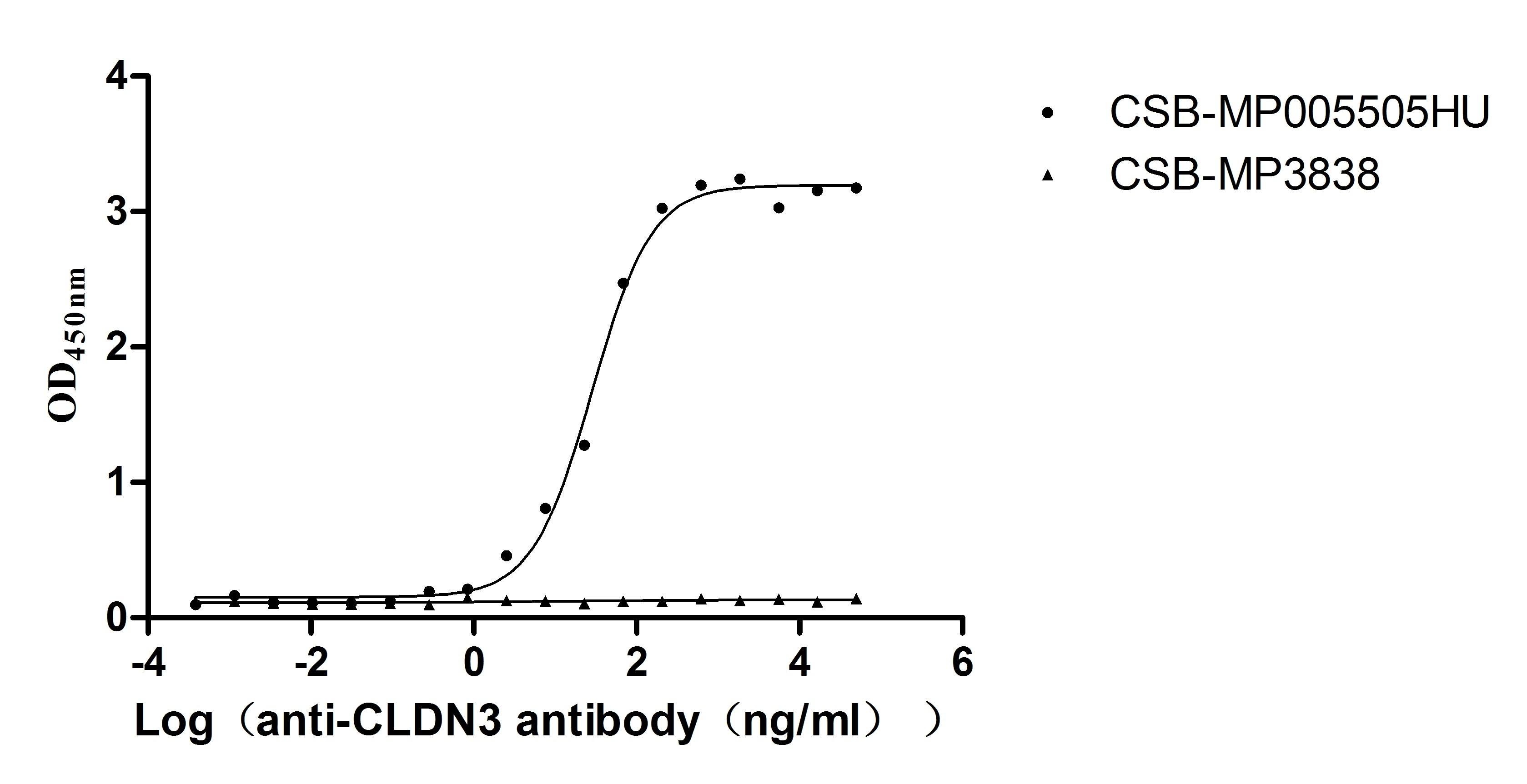
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
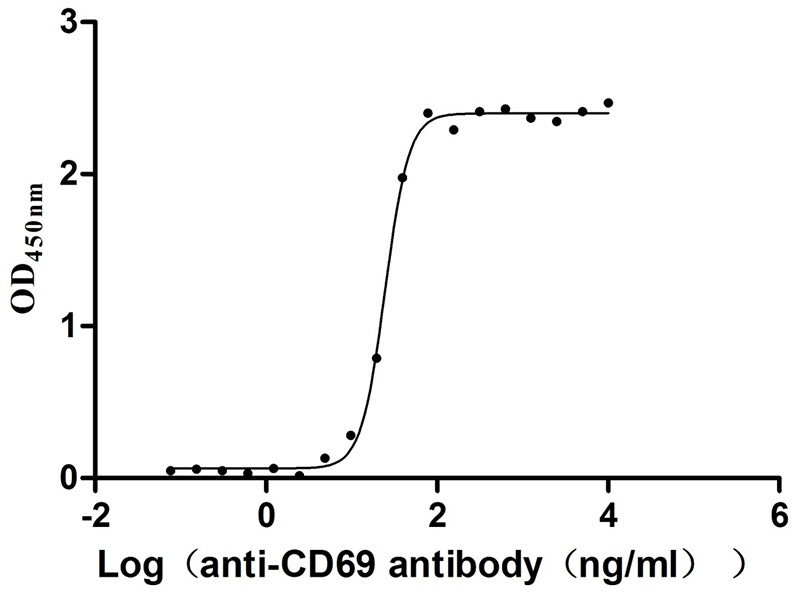
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
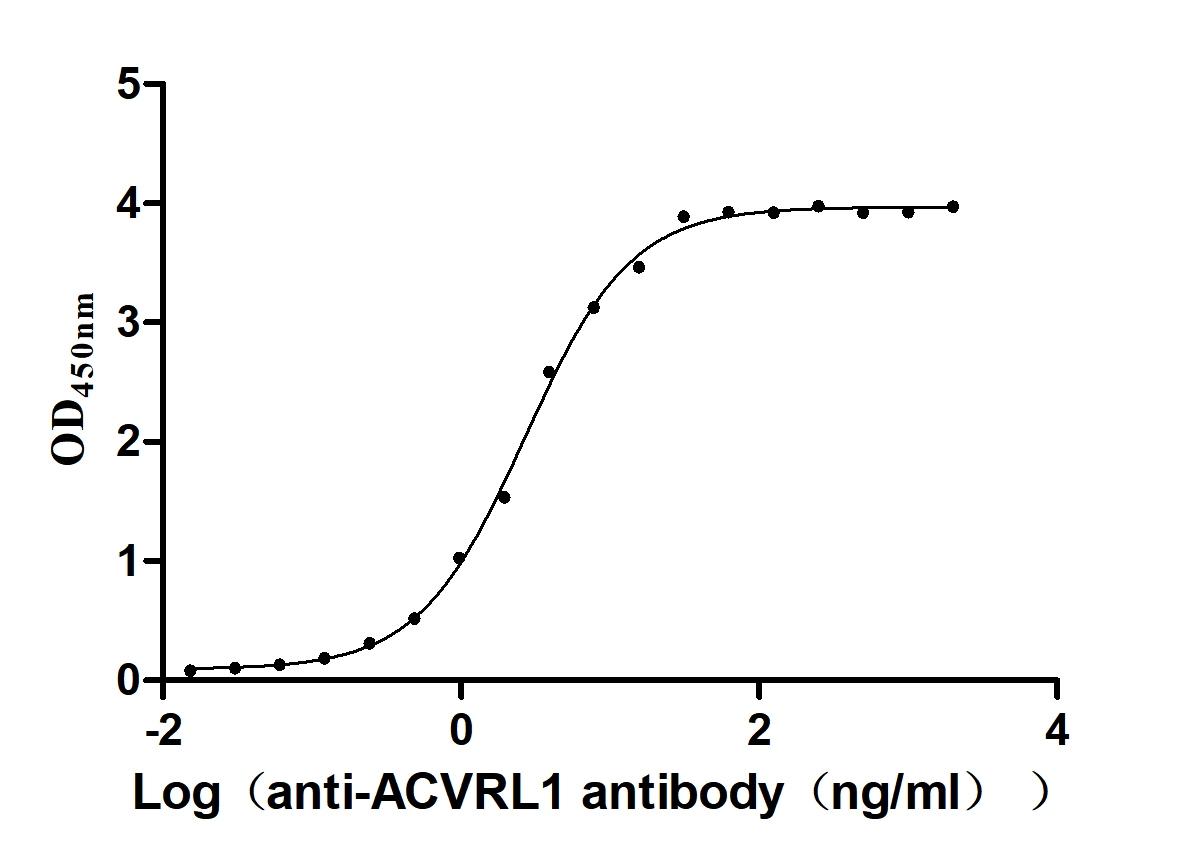
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

f4-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)