-
中文名稱:GIF1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA781430XA01DOA
-
規(guī)格:¥440
-
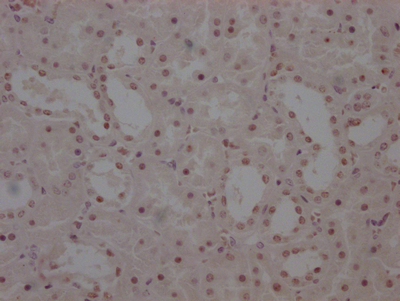
圖片:
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:GIF1
-
別名:GRF1-interacting factor 1 (AtGIF1) (Protein ANGUSTIFOLIA 3) (Transcription coactivator GIF1) GIF1 AN3 GIF At5g28640 F4I4.20
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Arabidopsis thaliana
-
免疫原:Recombinant Arabidopsis thaliana GIF1 protein (1-210aa)
-
免疫原種屬:Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
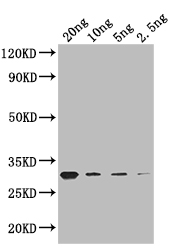
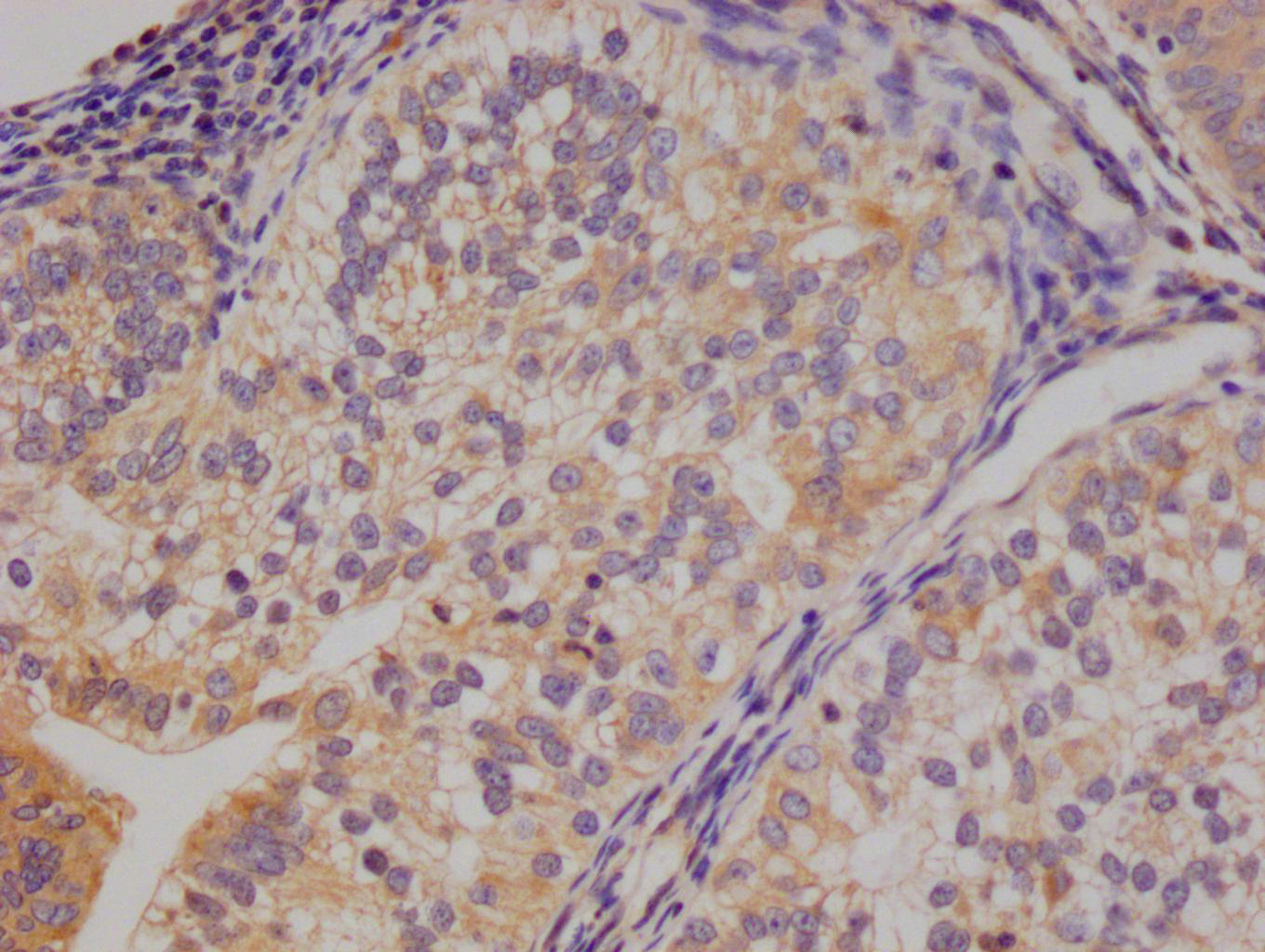
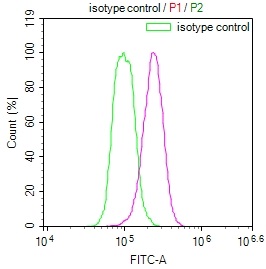
應(yīng)用范圍:ELISA, WB
-
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Transcription coactivator that plays a role in the regulation of cell expansion in leaf and cotyledons tissues. Component of a network formed by miR396, the GRFs and their interacting factors (GIFs) acting in the regulation of meristem function, at least partially through the control of cell proliferation. Appears to function synergistically with GRF1 as a transcriptional coactivator. Acts together with GRF5 for the development of appropriate leaf size and shape through the promotion and/or maintenance of cell proliferation activity in leaf primordia. Plays a role in adaxial/abaxial patterning and growth in leaf morphogenesis. GIFs are involved in the positive regulation of cell proliferation of lateral organs in a functionally redundant manner. Together with GATA18/HAN, mediates cotyledon identity by preventing ectopic root formation through the repression of PLT1 expression.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- GRF-GIF duo regulates the meristematic and pluripotent competence of carpel margin meristems. PMID: 29114079
- Rice MKB3 and Arabidopsis AN3 have conserved functions and effects on leaf development PMID: 29567670
- AN3 and YDA mutations both disrupt normal sucrose and glucose contents and cause altered seed size in an3 or yda mutants. PMID: 28489361
- Nuclear localization of AN3 during initial leaf growth results in differential expression of important transcriptional regulators, including GROWTH REGULATING FACTORs (GRFs). PMID: 24443518
- ANGUSTIFOLIA3 (AN3) moves into Arabidopsis epidermal cells after being synthesized within mesophyll cells and helps control epidermal cell proliferation. Interference with AN3 movement results in abnormal leaf size and shape. PMID: 23602479
- AN3 and AtGRF5 act together and are required for the development of appropriate leaf size and shape through the promotion and/or maintenance of cell proliferation. [AN3] PMID: 15960617
- Data found that an3-dependent compensation is a non-cell-autonomous process, and that an3 cells seem to generate and transmit an intercellular signal that enhances postmitotic cell expansion. PMID: 21068059
- Overexpression of miR396 in a mutant lacking GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR 1 severely compromises the shoot meristem. PMID: 20023165
- The GIF gene family plays important roles in the control of cell proliferation via cell cycle regulation and in other developmental properties that are associated with shoot apical meristem function. PMID: 19648231
顯示更多
收起更多
-
蛋白家族:SS18 family
-
組織特異性:Strongly expressed in actively growing and developing tissues, such as roots, upper stems, and shoot tips and flower buds. Also expressed in mature flowers. Not expressed in the shoot apical meristem (SAM). Highly accumulated in the proximal part of leaf
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-