Recombinant Arabidopsis thaliana Auxin efflux carrier component 1 (PIN1), partial
-
中文名稱:擬南芥PIN1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP883692DOA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:擬南芥PIN1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP883692DOA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:擬南芥PIN1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP883692DOA-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:擬南芥PIN1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP883692DOA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:擬南芥PIN1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP883692DOA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
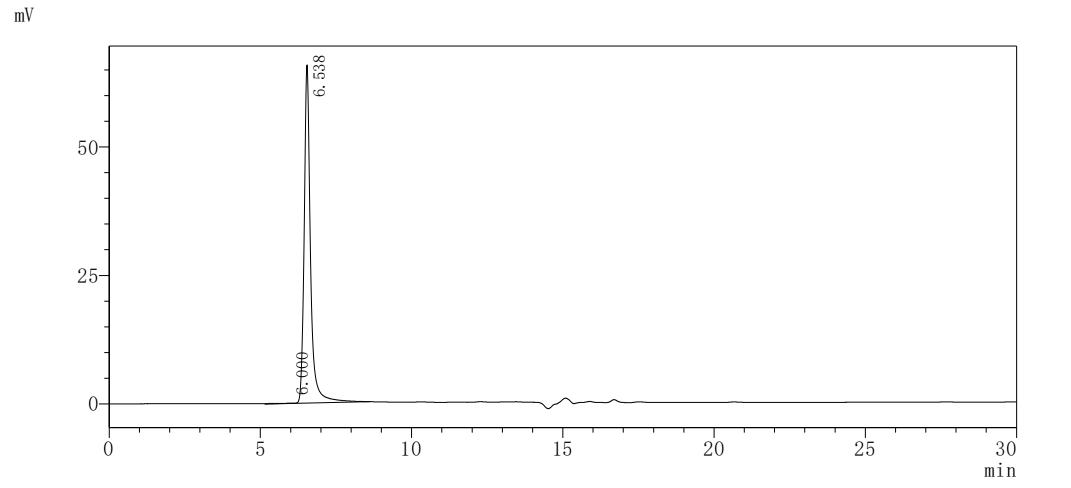
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PIN1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:PIN1; At1g73590; F6D5.2; Auxin efflux carrier component 1; Protein PIN-FORMED; AtPIN1
-
種屬:Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Acts as a component of the auxin efflux carrier. Seems to be involved in the basipetal auxin transport. Mediates the formation of auxin gradient which is required to ensure correct organogenesis. Coordinated polar localization of PIN1 is directly regulated by the vesicle trafficking process and apical-basal PIN1 polarity also depends on the phosphorylation of conserved serine residues by PID kinase. The ARF-GEF protein GNOM is required for the correct recycling of PIN1 between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartments.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Light triggers PIN1 polar membrane localization. PMID: 29284741
- PIN1 phosphorylation at S1-S4 was detected in situ using phosphosite-specific antibodies. Pin 1 phosphorylation at phosphosites at the basal as well as the apical plasma membrane in different root cell types, in embryos, and shoot apical meristems followed the predominant PIN1 distribution but was not restricted to specific polar sides of cells. Different protein kinases or trafficking mechanisms are involved. PMID: 28096328
- Phe-165, through the binding of muA (mu2)- and muD (mu3)-adaptin, is important for PIN1 endocytosis and for PIN1 trafficking along the secretory pathway, respectively. PMID: 27208248
- protein topology of plasma membrane-localized PINs PMID: 27622590
- The authors propose that PIN1 expression mediated by cytokinin response factors are required for the determination of pistil size. The greater number of ovule primordia in cytokinin-treated pistils correlates with the increased pistil size. when enough space occurs between two ovules, cytokinin response factors and/or other cytokinin-dependent factors induce PIN1 expression to create a new auxin maximum. PMID: 27737904
- comprehensive 3D analysis of PIN1 expression patterns in Arabidopsis thaliana roots PMID: 26821586
- Cell-type-specific expression of a constitutively active form of BZR1 confirms that the high and low levels of BZR1 are required for the normal cell behaviors in the elongation zone and quiescent center. PMID: 25866388
- Myrosin cell development requires the endocytosis-mediated polar localization of the auxin-efflux carrier PIN1 in leaf primordial. PMID: 25428982
- Functional interplay between protein kinase CK2 and salicylic acid sustains PIN1 transcriptional expression. PMID: 24547808
- In development of interfascicular cambium from differentiated interfascicular parenchyma cells, the events are: appearance of auxin accumulation, PIN1 gene expression, polar PIN1 protein localization in the basal plasma membrane and periclinal divisions. PMID: 24526327
- ARF1A1C is essential for recycling of PIN auxin transporters and for various auxin-dependent developmental processes. PMID: 24369434
- Blue light-induced PIN1 redistribution participates in asymmetric auxin distribution and root negative phototropism. PMID: 24465665
- Copper (Cu)-mediated auxin redistribution was shown to be responsible for Cu-mediated inhibition of primary root elongation and PINFORMED1 (PIN1), but not PIN2 or AUXIN1 (AUX1), that regulated this process. PMID: 23396597
- Epigenetic regulation may control auxin-mediated lateral root development through the 26S proteasome-mediated degradation of PIN1 protein. PMID: 23820978
- PIN1 expression in the miristem L1 is sufficient for correct phyllotaxis. PMID: 24091013
- polarity of the auxin efflux carrier PIN1 and auxin distribution, determined with the DR5(pro):GFP proxy, are affected by mutations in PP2A-C3 and PP2A-C4. PMID: 23167545
- Cytokinin regulates ovule development through the regulation of PIN1. PMID: 22786869
- PIN1 phosphorylation is directly regulated by PP6-type phosphatase holoenzyme PMID: 22715043
- PIN1 and PIN2 proteins show dynamic intracellular trafficking and polar localization in the plasma membrane. PMID: 22492845
- use of both chemical treatments and mutants with altered NO levels demonstrates that high levels of NO reduce auxin transport and response by a PIN1-dependent mechanism, and root meristem activity is reduced concomitantly PMID: 22021439
- Our findings suggest a common mechanism for the regulation of PIN1 polarity formation, a fundamental cellular process that is crucial for pattern formation both at the tissue/organ and cellular levels PMID: 21423279
- Data suggest that FKD1 influences PIN1 localization in an auxin-dependent manner, and we propose that it represents a key component of the auxin canalization pathway. PMID: 20626652
- Data reveal that both PIN1 localization and microtubule array orientation are likely to respond to a shared upstream regulator that appears to be biomechanical in nature. PMID: 20976043
- Loss of PIN1 phosphorylation at the conserved Ser residues induces dominant embryo and flower phenotypes. PMID: 20407025
- NOV is required for provascular PIN1 expression. PMID: 19880797
- Different levels of indole acetic acid in the stems and flowers of A. thaliana plants with a mutation at PIN1 are reported. PMID: 15918026
- findings revealed that the action of PINs in auxin efflux is distinct from phosphoglycoprotein, rate-limiting, specific to auxins, and sensitive to auxin transport inhibitors; this suggests a direct involvement of PINs in catalyzing cellular auxin efflux PMID: 16601150
- subcellular distribution is gradually refined from a non-polar distribution in isodiametric cells to strongly polarized in elongated procambial cells and provides an indication of overall directions of auxin flow PMID: 17217464
- Inducible JLO misexpression activates expression of the KNOX genes SHOOT MERISTEMLESS and KNAT1 in leaves and downregulates the expression of PIN auxin export facilitators. PMID: 17557810
- Results show that in addition to pathways that control PIN localization and transcription, MOP2 and MOP3 appear to be involved in fine-tuning of auxin distribution via post-transcriptional regulation of PIN expression. PMID: 17651372
- flavonoids promote asymmetric PIN1,2 shifts during gravity stimulation, thus redirecting basipetal auxin streams necessary for root bending. PMID: 18718912
- VAM3 is required for the proper expression pattern of PIN1, and PIN1 proteins are constitutively transported to vacuoles in leaf and roots cells. PMID: 19493960
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Auxin efflux carrier (TC 2.A.69.1) family
-
組織特異性:Expressed at the basal side of elongated parenchymatous xylem cells.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
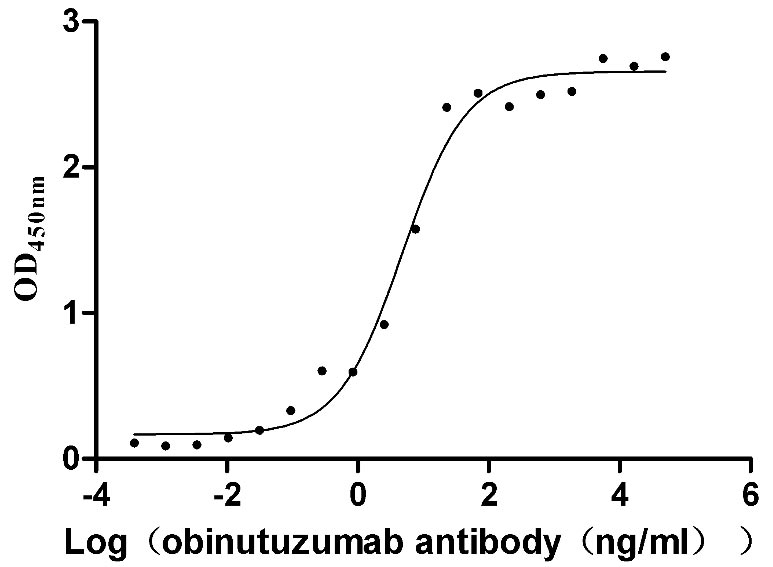
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Claudin-18.2 (Cldn18.2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
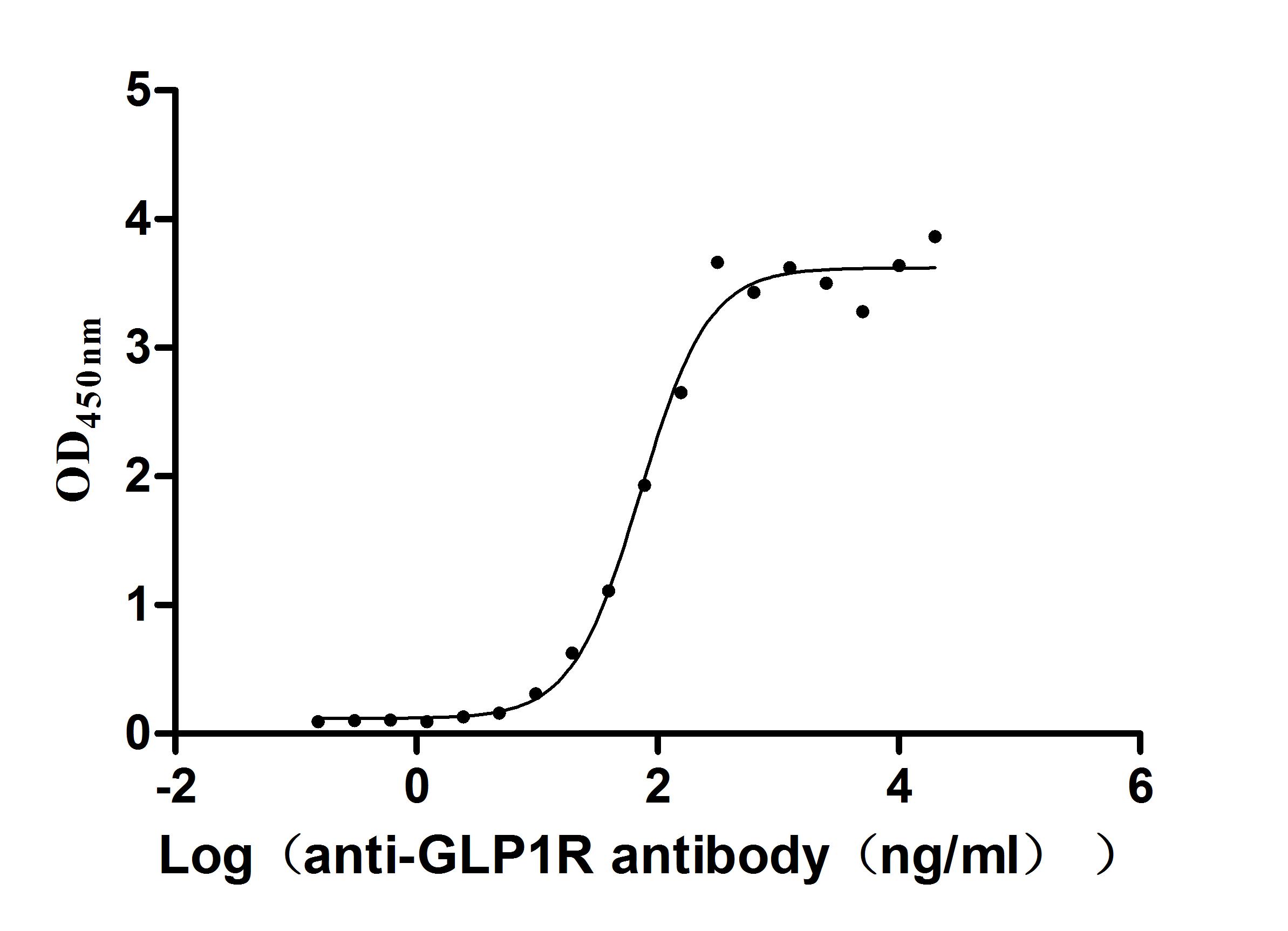
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
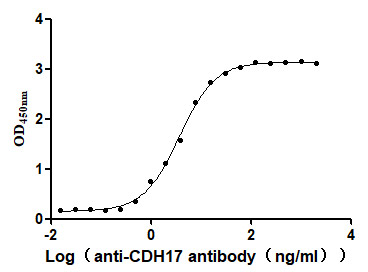
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
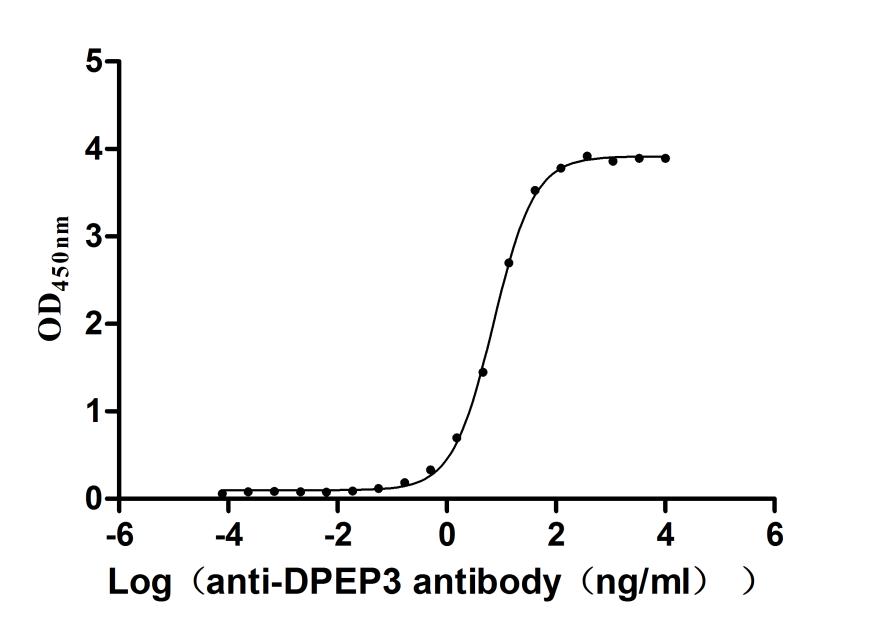
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

-AC1.jpg)