Recombinant Human Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM9 (PRDM9), partial
-
中文名稱:人PRDM9重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP885695HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PRDM9重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP885695HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PRDM9重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP885695HU-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PRDM9重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP885695HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:人PRDM9重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP885695HU
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:PRDM9
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:EC 2.1.1.43; Histone lysine N methyltransferase PRDM9; Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM9; MEISETZ; PFM6; PR domain containing 9; PR domain containing protein 9; PR domain zinc finger protein 9; PR domain-containing protein 9; PRDM 9; PRDM9; PRDM9_HUMAN
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Histone methyltransferase that sequentially mono-, di-, and tri-methylates both 'Lys-4' (H3K4) and 'Lys-36' (H3K36) of histone H3 to produce respectively trimethylated 'Lys-4' (H3K4me3) and trimethylated 'Lys-36' (H3K36me3) histone H3 and plays a key role in meiotic prophase by determining hotspot localization thereby promoting meiotic recombination. Also can methylate all four core histones with H3 being the best substrate and the most highly modified. Is also able, on one hand, to mono and di-methylate H4K20 and on other hand to trimethylate H3K9 with the di-methylated H3K9 as the best substrate. During meiotic prophase, binds specific DNA sequences through its zinc finger domains thereby determining hotspot localization where it promotes local H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 enrichment on the same nucleosomes through its histone methyltransferase activity. Thereby promotes double-stranded breaks (DSB) formation, at this subset of PRDM9-binding sites, that initiates meiotic recombination for the proper meiotic progression. During meiotic progression hotspot-bound PRDM9 interacts with several complexes; in early leptonema binds CDYL and EHMT2 followed by EWSR1 and CXXC1 by the end of leptonema. EWSR1 joins PRDM9 with the chromosomal axis through REC8. In this way, controls the DSB repair pathway, pairing of homologous chromosomes and sex body formation. Moreover plays a central role in the transcriptional activation of genes during early meiotic prophase thanks to H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 enrichment that represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation. In addition performs automethylation. Acetylation and phosphorylation of histone H3 attenuate or prevent histone H3 methylation.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- These results support the hypothesis that ow-copy repeats 22 variations influences 22q11.2 non-allelic homologous recombination events, however further studies are needed to confirm this association and clarify the contribution of pseudogenes and rare PDRM9 alleles to non-allelic homologous recombination susceptibility for DiGeorge/velocardiofacial syndrome. PMID: 28059126
- Finally, the authors demonstrate that, in addition to binding DNA, PRDM9's zinc fingers also mediate its multimerization, and they show that a pair of highly diverged alleles preferentially form homo-multimers. PMID: 29072575
- The most common genetic variant of PRDM9 is allele A (PRDM9a) which contains 13 Cys2-His2 zinc fingers (ZF); the second-most common variant among African populations is allele C (PRDM9c), which contains 14 Cys2-His2 ZF. Data suggest that Ser764 in ZF9 allows PRDM9c to accommodate a variable base, whereas PRDM9a Arg764 recognizes a conserved guanine. PMID: 28801461
- The article outlines the role of PRDM9 in fertility. PMID: 27045445
- Allele C was found to bind a C-specific hot spot with higher affinity than allele A bound A-specific hot spots PMID: 26833727
- PRDM9 protein variants form functional heteromeric complexes which can bind hotspots sequences. When a heteromeric complex binds at a hotspot of one PRDM9 variant, the other PRDM9 variant, which would otherwise not bind, methylates hotspot nucleosomes PMID: 26368021
- subspecies-specific degradation of PRDM9 binding sites by meiotic drive, which steadily increases asymmetric PRDM9 binding, has impacts beyond simply changing hotspot positions, and strongly support a direct involvement in hybrid infertility PMID: 26840484
- Alignment of Neandertal and Denisovan sequences suggests that PRDM9 in archaic hominins was closely related to present-day human alleles that are rare and specific to African populations. PMID: 25001002
- This depletion of PRDM9 genomic targets is expected to decrease fitness, and thereby to favor new PRDM9 alleles binding different motifs PMID: 25393762
- Results confirm an association between rare variant PRDM9 alleic forms and childhood ALL PMID: 24754746
- Overexpression of PRDM9 in HEK293 cells also resulted in a significant increase in trimethylated H3K36 and H3K4 further confirming our in vitro observations PMID: 24634223
- We identified PRDM9 as being associated with unusual recombination patterns and discovered a substantial excess of rare allelic forms of PRDM9 in two independent acute lymphoblastic leukemia cohorts. PMID: 23222848
- Recombination regulator PRDM9 influences the instability of its own coding sequence in humans. PMID: 23267059
- observed a increased frequency of PRDM9 variants in parents who transmitted de novo 7q11.23 deletions to their offspring. These data suggest that certain PRDM9 alleles may be associated with an increased susceptibility to recurrent 7q11.23 microdeletions PMID: 22643917
- discussion of role of PRDM9 in meiotic recombination hotspots; consideration of the structure of the PRDM9 protein [REVIEW] PMID: 22162947
- Each African-enhanced hotspot is activated by a distinct spectrum of PRDM9 variants, despite the fact that all are predicted to bind the same motif. This differential activation points to complex interactions between the zinc-finger array and hotspots. PMID: 21750151
- PRDM9 variation strongly influences recombination hot-spot activity and meiotic instability. PMID: 20818382
- Human coding polymorphism and interspecies evolutionary changes in the PRDM9 gene, was analyzed. PMID: 20041164
- sequence of exon 12 of PRDM9; human populations exhibit two predominant alleles and multiple minor alleles of Prdm9 PMID: 20044538
- results provide a molecular basis for the distribution of meiotic recombination in mammals in which the binding of PRDM9 to specific DNA sequences targets the initiation of recombination at specific locations in the genome PMID: 20044539
- findings implicate the PRDM9 gene in meiotic recombination; involvement of PRDM9, which causes histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation, implies that there is a common mechanism for recombination hotspots in eukaryotes PMID: 20044541
- Results show a possible association between PRDM9 and azoospermia by meiotic arrest. PMID: 18941885
- Our results suggest that mutations in PRDM9 may cause idiopathic infertility in human males. PMID: 19168450
- Evolutionary analysis suggests that human PRDM7 and PRDM9 genes, a pair of close paralogs corresponding to a single mouse gene Prdm9, were generated by a recent gene duplication event after the divergence of the ancestors of human and mouse. PMID: 18231586
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus. Chromosome.
-
蛋白家族:Class V-like SAM-binding methyltransferase superfamily
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
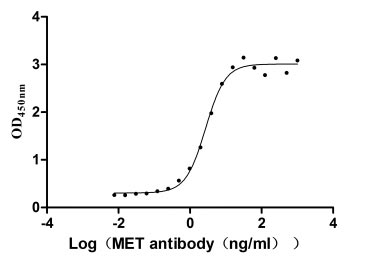
Recombinant Human Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
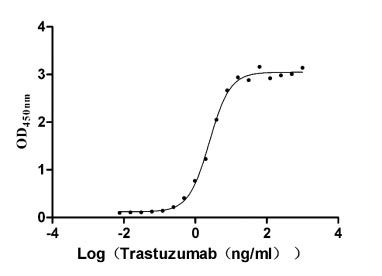
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
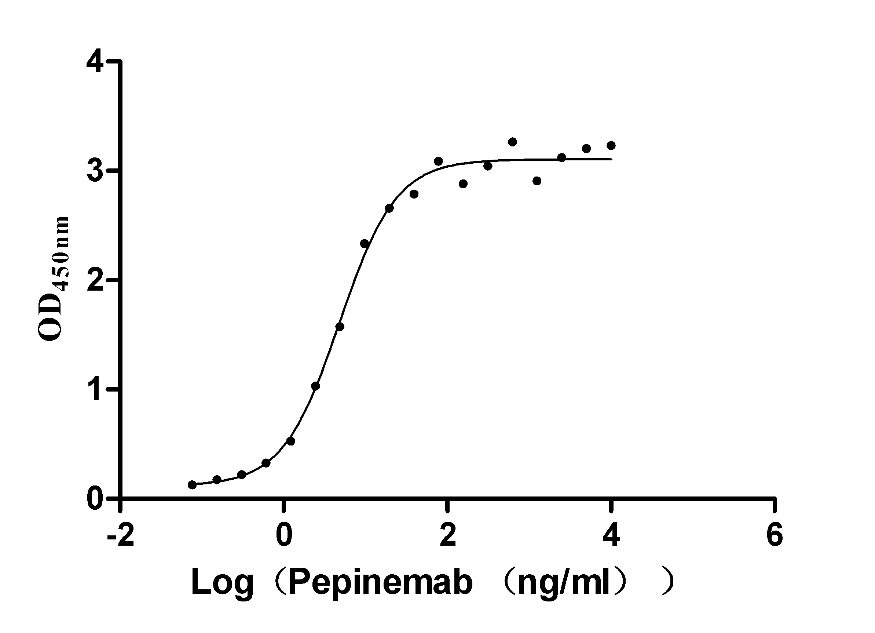
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
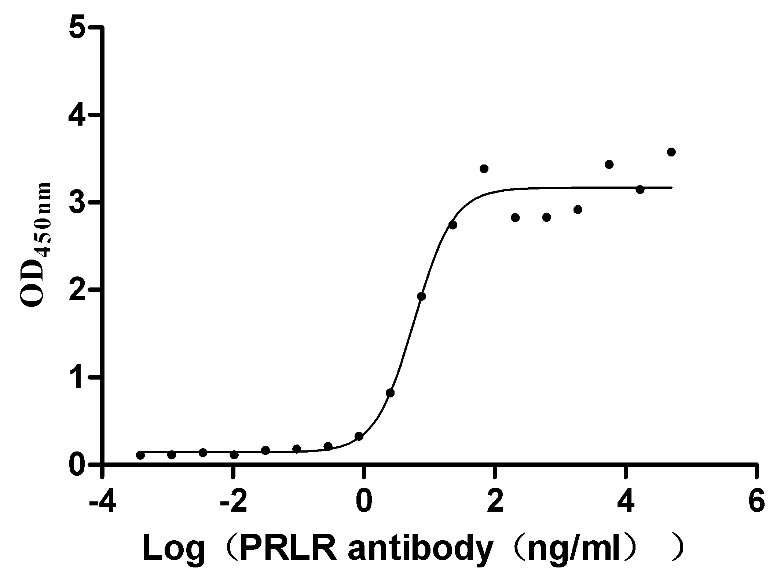
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
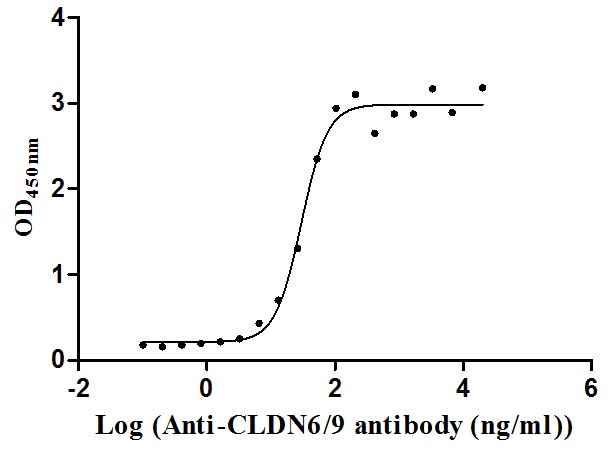
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
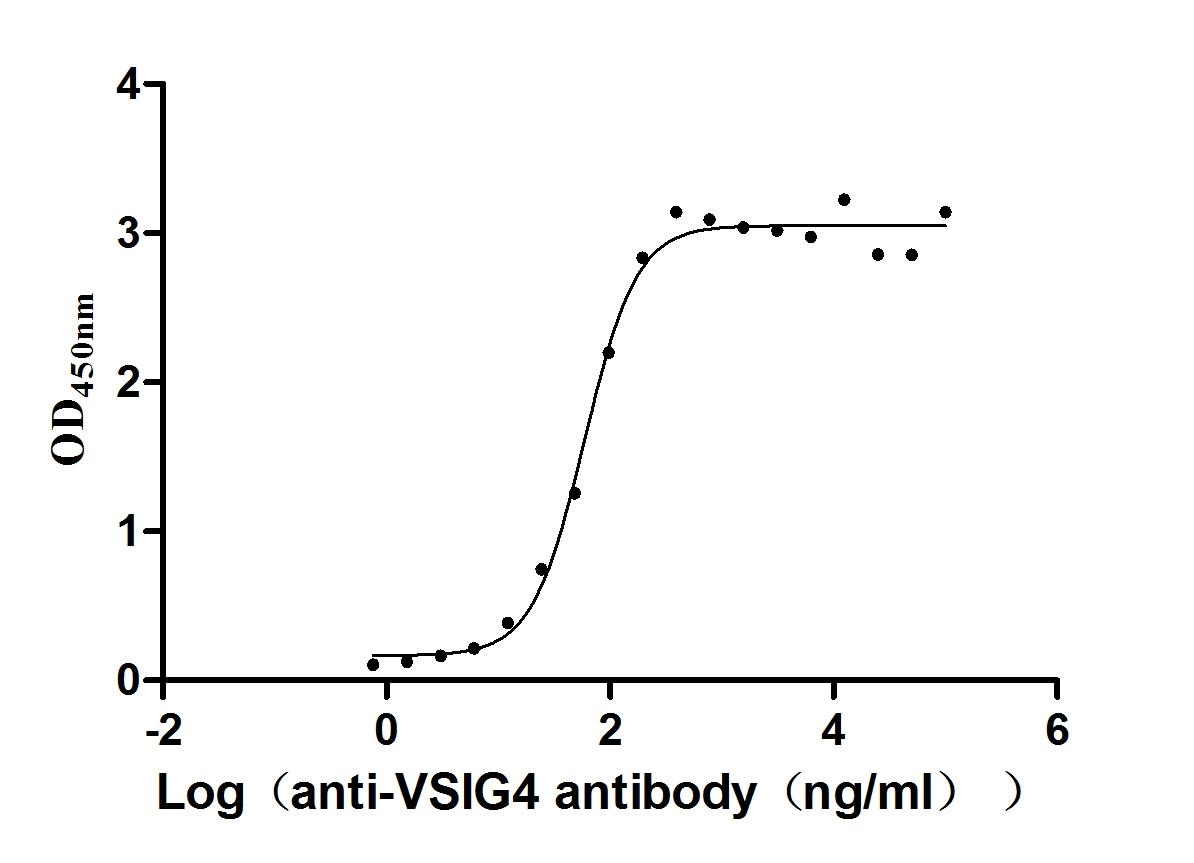
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)