Recombinant Mouse Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 (Med1), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Med1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP849768MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Med1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP849768MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Med1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP849768MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Med1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP849768MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Med1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP849768MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Med1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Med1; Crsp210; Drip205; Pbp; Pparbp; Trap220; Trip2; Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1; Mediator complex subunit 1; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein; PBP; PPAR-binding protein; Thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex 220 kDa component; Trap220; Thyroid receptor-interacting protein 2; TR-interacting protein 2; TRIP-2
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Component of the Mediator complex, a coactivator involved in the regulated transcription of nearly all RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. Mediator functions as a bridge to convey information from gene-specific regulatory proteins to the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Mediator is recruited to promoters by direct interactions with regulatory proteins and serves as a scaffold for the assembly of a functional preinitiation complex with RNA polymerase II and the general transcription factors. Essential for embryogenesis, including development of the central nervous system, heart, liver and placenta and for erythropoiesis. Also required for normal transcriptional control of thyroid-stimulating hormone beta (TSHB) in the pituitary. Acts as a coactivator for GATA1-mediated transcriptional activation during erythroid differentiation of K562 erythroleukemia cells.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- High MED1 expression is associated with metastasis in breast Cancer. PMID: 29187405
- Data, including data from studies using cells from transgenic/knockout mice, suggest that Med1 plays role in enamel formation; Med1 induces Alpl via stimulation of Notch1 signaling by forming Notch1-RBP-Jk complex on Alpl promoter. (Med1 = mediator complex subunit 1; Alpl = alkaline phosphatase, liver-bone-kidney; Notch1 = Notch gene homolog 1; RBP-Jk = kappa J region recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless) PMID: 28673966
- MED1 in macrophages has an antiatherosclerotic role via PPARgamma-regulated transactivation. PMID: 28642237
- Cardiomyocyte-specific ablation of Med1 causes lethal dilated cardiomyopathy in mice. PMID: 27548259
- Med1 deletion disrupted cardiac mitochondrial and metabolic gene expression patterns PMID: 28159809
- Med1 and Med12, two subunits of the mediator complex implicated in transcription initiation and long-range enhancer/promoter loop formation, are dynamically recruited to the IgH locus enhancers. PMID: 26903242
- We conclude that MED1 regulates the temporal progression of primary spermatocytes through meiosis, with its absence resulting in abbreviated pre-leptotene, leptotene, and zygotene stages, and a prolonged pachytene stage. PMID: 25778538
- These results demonstrate that Med1 is a master regulator in adult stem cells to govern epithelial cell fate PMID: 24949995
- The novel function of MED1 in keratinocytes. PMID: 25122137
- PRDM16 deficiency in BAT reduces MED1 binding at PRDM16 target sites and causes a fundamental change in chromatin architecture at key brown fat-selective genes PMID: 25644604
- Collectively, these observations strongly suggest that MED1 has an important affect on mitochondrial function. PMID: 24368311
- Clk2 phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha disrupts its interaction with Mediator subunit 1, which leads to a suppression of PGC-1alpha activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes in fatty acid oxidation and ketogenesis. PMID: 24458359
- hyperactivated ERK and/or AKT signaling pathways promoted MED1 overexpression in prostate cancer cells. PMID: 23538858
- Tshb gene transcription was attenuated in MED1 mutant mice in which the nuclear receptor-binding ability of MED1 was specifically disrupted. PMID: 24055033
- Med1 is a context-dependent GATA-1 coregulator that also exerts specialized functions in erythroid cells to control GATA-1-independent, cell-type-specific genes. PMID: 23459945
- MED1 has roles in maintaining quiescence of keratinocytes and preventing depletion of the follicular stem cells. PMID: 22931914
- Hyperlipidemia in MED1(deltaLiv) mice in response to fasting is due to the accumulation of VLDL, which suggests that MED1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of plasma triglyceride and cholesterol levels. PMID: 22260066
- Med1 is implicated in adipogenesis, lipid metabolic and biosynthetic processes, glucose metabolism, and mitochondrial metabolic pathways PMID: 22570438
- functional communications between the MED1 subunit and the MED24-containing submodule that mediate estrogen receptor functions and growth of both normal mammary epithelial cells and breast carcinoma cells PMID: 22331469
- MED1 has a critical role in regulating hair/epidermal proliferation and differentiation. PMID: 22189783
- T-cell-specific Med1 deficiency results in a specific block in iNKT cell development but the development of conventional alphabeta T cells remains grossly normal. PMID: 21949387
- We conclude that transcription coactivator MED1 is required for high-fat diet-induced and PPARgamma-stimulated fatty liver development, which suggests that MED1 may be considered a potential therapeutic target for hepatic steatosis. PMID: 21480322
- Data suggest that Mediator subunit Med1 plays a pivotal role in erythroid development and in beta-globin gene activation. PMID: 21098667
- MED1 appears to play an important role in supporting hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells by upregulating VDR- and Runx2-mediated transcription on the Opn promoter. PMID: 20713445
- skeletal muscle-specific Med1 knockout mice show enhanced insulin sensitivity and improved glucose tolerance as well as resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity PMID: 20479251
- MED1 LxxLL motifs have a key nuclear receptor- and cell-specific in vivo role through Mediator-ERalpha interactions, in mammary gland development PMID: 20351249
- TRAP/Mediator directly facilitates ER function. PMID: 11867769
- Trap220(-/-) fibroblasts are refractory to PPAR gamma(2)-stimulated adipogenesis PMID: 12037571
- TRAP220 plays an important role in growth and differentiation of central nervous system and may have a function in certain areas of adult brain. PMID: 12270043
- PBP is required for the successful completion of the adipogenic program PMID: 12754253
- Requirement for TRAP220 in extraembryonic tissues at E11.5, with an additional requirement in embryonic tissues for hepatic and cardiovascular development thereafter. PMID: 14500757
- coactivator PBP is essential for PPARalpha-regulated gene expression in liver parenchymal cells PMID: 15150259
- Transfection studies using TRAP220 mutants revealed that the N terminus of TRAP220 is necessary and sufficient for stable association with the TRAP/Mediator complex. PMID: 15340084
- PBP plays a pivotal role in the normal mammary gland development PMID: 15647257
- The role of transcriptional coactivator TRAP220 in myelomonocytic differentiation PMID: 16324150
- Results establish that transcription coactivator PBP plays a pivotal role in nuclear localization of constitutive androstane receptor. PMID: 16828057
- Through expression profiling of SS18 knockout embryos, we observed altered expression of genes known to affect placental development, including the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein (Pparbp). PMID: 16926188
- critical role of PBP/TRAP220 in liver regeneration, induction of hepatotoxicity, and hepatocarcinogenesis PMID: 17438330
- there is a conditional requirement for MED1 and that a direct interaction between PPARgamma and Mediator through MED1 is not essential either for PPARgamma-stimulated adipogenesis or for PPARgamma target gene expression in CULTURED fibroblasts PMID: 18039840
- ERK-regulated site in Med1 protein is also essential for up-regulating interferon-induced transcription although not critical for binding to C/EBP-beta PMID: 18339625
- The A/B-domain of PPARgamma2 is specifically involved in the recruitment or stabilization of CBP- and p300-containing cofactor complexes to a subset of target genes. PMID: 19282365
- Absence of MED1 in the liver diminishes Dex-induced hepatic steatosis by altering the GR- and CAR-dependent gene functions. PMID: 19630272
- Report dynamic interactions and cooperative functions of PGC-1alpha and MED1 in TRalpha-mediated activation of the brown-fat-specific UCP-1 gene. PMID: 19782026
- MED1/TRAP220 is the nuclear receptor-interacting subunit of the Mediator complex and is required for PPARgamma-stimulated adipogenesis. PMID: 12037571
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Mediator complex subunit 1 family
-
組織特異性:Widely expressed in the adult, with high levels of expression in the liver, lung, intestinal mucosa, kidney cortex, thymic cortex, splenic follicle and seminiferous epithelium in testis. Also expressed in the adult heart, brain, spleen and skeletal muscle
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
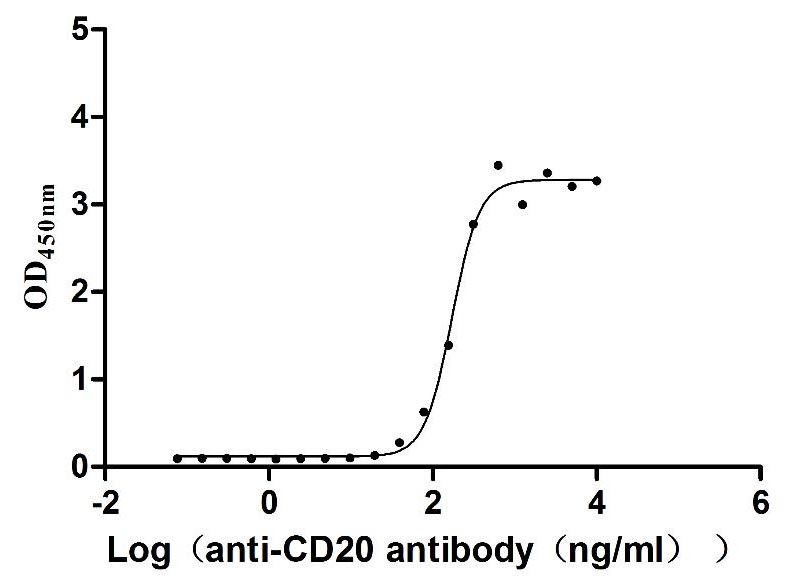
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
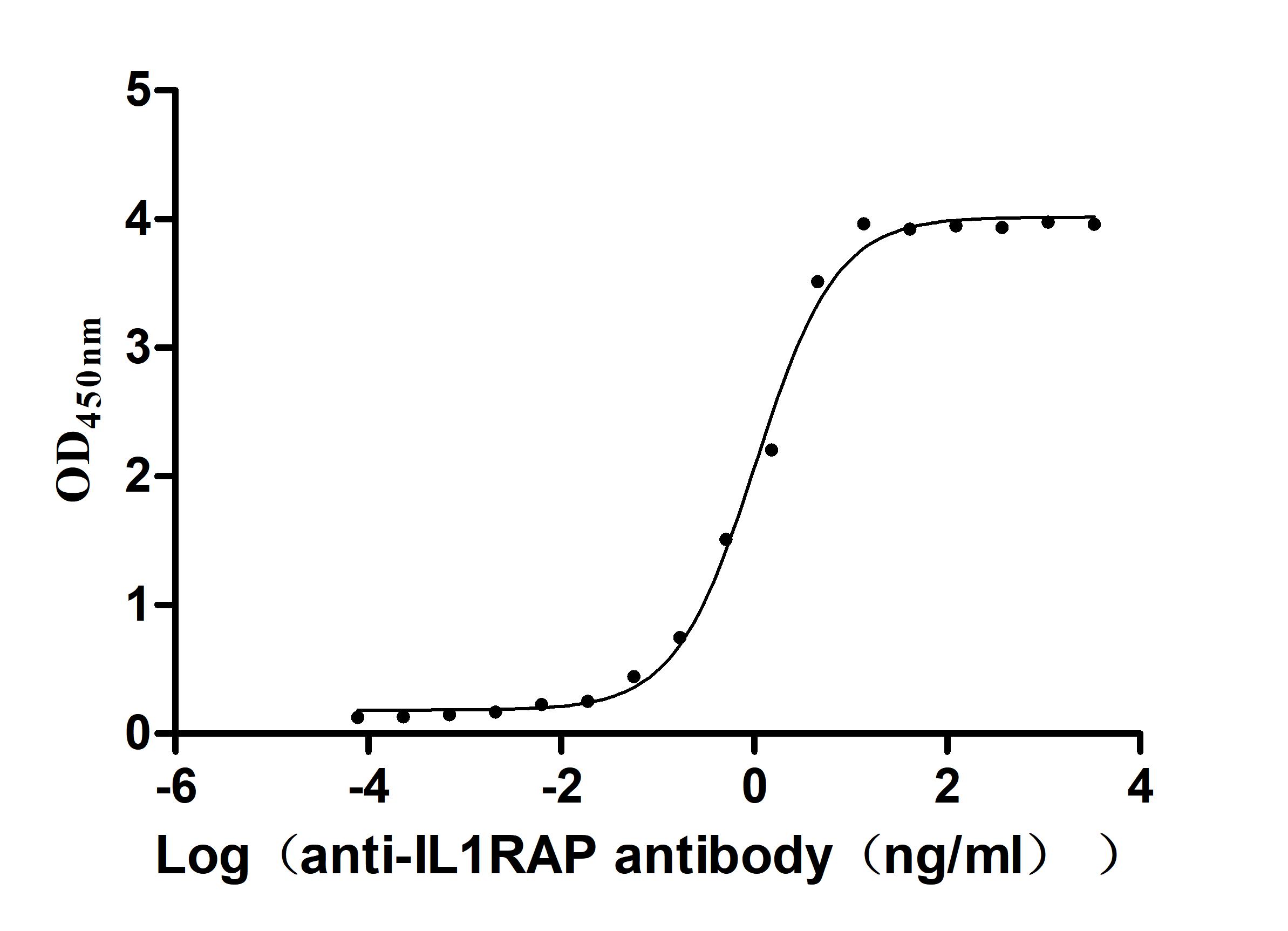
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)

-AC1.jpg)