Recombinant Mouse Sodium channel protein type 11 subunit alpha (Scn11a), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn11a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP874155MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn11a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP874155MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn11a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP874155MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn11a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP874155MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn11a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP874155MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Scn11a
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Scn11a; Nan; Nat; Sns2Sodium channel protein type 11 subunit alpha; NaN; Sensory neuron sodium channel 2; Sodium channel protein type XI subunit alpha; Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1.9
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel isoform. Also involved, with the contribution of the receptor tyrosine kinase NTRK2, in rapid BDNF-evoked neuronal depolarization.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- This study demonstrated that NaV1.9 presumably contributes to acute thermal and mechanical nociception in mice. PMID: 27780178
- Recently Nav1.9, a voltage-gated sodium channel subtype, has been established as a genetic influence for certain peripheral pain syndromes. PMID: 27224030
- A missense mutation (p.V1184A) in NaV1.9 leads to cold-aggravated peripheral pain. PMID: 26645915
- We conclude that Nav1.9 acts as a subthreshold amplifier in cold-sensitive nociceptive neurons and is required for the perception of cold pain under normal and pathological conditions. PMID: 25959819
- NaV1.9 is required for persistence of responses to intense mechanical stimulation, contributes to inflammatory mechanical hypersensitivity, and is essential for activation by noxious inflammatory mediators, including those from diseased human bowel. PMID: 24972070
- The results strongly suggested that Nav1.9 was expressed and functionally contributed to the signaling processing in the central auditory pathway. PMID: 25385328
- Axon growth of NaV1.9-deficient motoneurons in cell culture is drastically reduce. PMID: 23238424
- In the stable NaV1.9-deficient cells we successfully constructed, proliferation, phagocytosis and migration were obviously inhibited. PMID: 23643074
- Na(V)1.9 function appears to be essential for activity-dependent axon growth in motor neurons, acting upstream of spontaneous Ca(2+) elevation through voltage-gated calcium channels. PMID: 22641814
- Results provide evidence that Nav1.9 plays a crucial role in the generation of heat and mechanical pain hypersensitivity, both in subacute and chronic inflammatory pain models. PMID: 21857998
- results indicate that the spontaneous augmentation of Na(V)1.9 was regulated directly by protein kinase A, and indirectly by protein kinase C PMID: 20411123
- The present study provides evidence for a modulatory role of Na(v)1.9 also indicate that Na(v)1.9 signaling might be involved in visceral pain. PMID: 19931571
- inflammatory mediators modify the function of NaV1.9 to maintain inflammation-induced hyperalgesia PMID: 15964986
- Hyperexcitability was maintained in Na(v)1.9(-/-) mice, but hyperexcitability was absent and APs were blunted in Na(v)1.8(-/-) mice. PMID: 16857712
- Nav1.9 is an effector of the hyperalgesia produced by inflammatory mediators and plays a role in mediating peripheral sensitization. PMID: 17167076
- potential role of Nav1.9 in the transmission of trigeminal pain and the regulation of intestinal reflexes PMID: 17363266
- an electrically induced signal can propagate along the vessel axis via the endothelium and can induce sequential activation of Na(v) and Ca(v)3.2 channels. PMID: 17513486
- Na(V)1.9 underlies the G-protein pathway-regulated TTX-r persistent Na(+) current in small diameter sensory neurones that may drive spontaneous discharge in nociceptive nerve fibres during inflammation. PMID: 18096591
- Na(v)1.9 channels do not significantly contribute to normal visceral pain responses to acute colonic mechanical stimulation but may be important for the development of inflammation-related acute visceral hyperalgesic responses. PMID: 18280187
- Na(v)1.9 is expressed by photoreceptors and Muller glia in retina f mice. PMID: 18399542
- Nav1.9 sodium channel provides an important link between inflammatory processes and changes in urodynamic properties that occur during urinary bladder inflammation. PMID: 19146922
- differential regulation of Scn11a and Trpm8 contributes to across-strain variability in pain phenotype PMID: 19228393
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Sodium channel (TC 1.A.1.10) family, Nav1.9/SCN11A subfamily
-
組織特異性:Expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (C-fiber neurons), spinal cord, trigeminal ganglia, testis, ovary, uterus and small intestine.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human T-cell antigen CD7 (CD7), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (MERTK), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
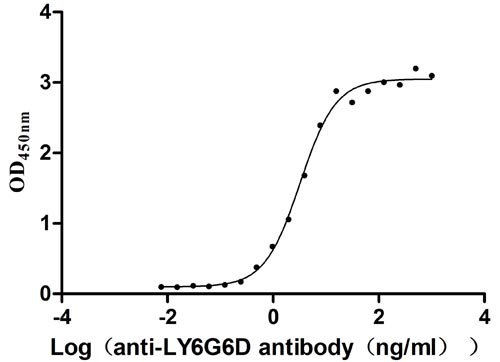
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
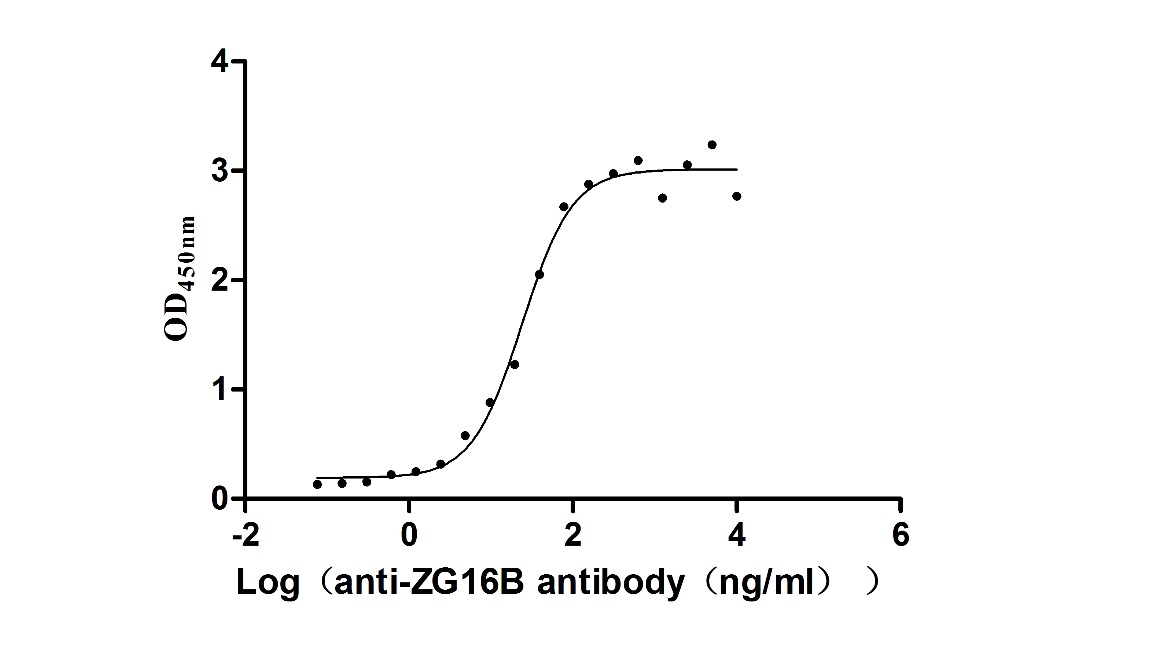
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
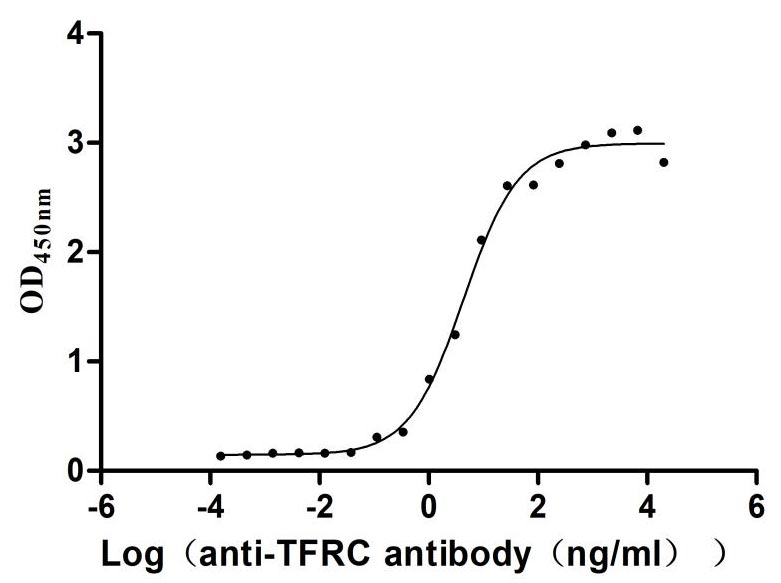
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
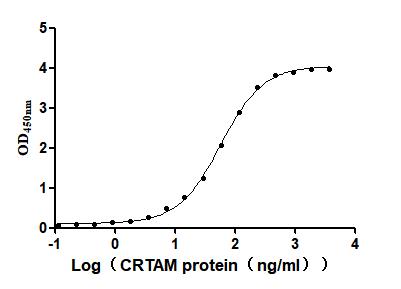
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)