Recombinant Mouse Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha (Scn5a), partial
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn5a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP878080MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn5a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP878080MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn5a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP878080MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn5a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP878080MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Scn5a重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP878080MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Scn5a
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Scn5a; Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein cardiac muscle subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein type V subunit alpha; Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1.5; mH1
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Partial
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential. Channel inactivation is regulated by intracellular calcium levels.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- The late sodium current inhibitor GS-458967 exhibits anti-arrhythmic potential in cardiac myocytes from Scn5a-1798insD+/- mice. PMID: 28430892
- Our findings indicate that H2O2 inhibits NaV1.5 expression by activating the Wnt/b-catenin signaling and beta-catenin interacts with TCF4 to transcriptionally suppress cardiac NaV1.5 expression. PMID: 27068063
- identified two novel native phosphorylation sites in the C terminus of NaV1.5 that impair FGF13-dependent regulation of channel inactivation and may contribute to CaMKIIdeltac-dependent arrhythmogenic disorders in failing hearts. PMID: 28882890
- Tetrodotoxin-sensitive alpha-subunits of voltage-gated sodium channels are relevant for inhibition of cardiac sodium currents by local anesthetics. PMID: 27000037
- Enhanced A-V conduction in mice overexpressing SCN5A in the heart mimics the human syndrome of Enhanced Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction . PMID: 25623181
- Loss of the C-terminus of connexin43 limits microtubule plus-end capture and NaV1.5 localization at the intercalated disc. PMID: 25139742
- Ser571-mediated increases in INa,L promote abnormal repolarization and intracellular Ca(2+) handling and increase susceptibility to arrhythmia. Ser571 is required for maladaptive remodeling and arrhythmias in response to pressure overload. PMID: 26187182
- intracellular Ca(2+) contributes to the regulation of INaL conducted by NaV1.5 mutants and propose that, during excitation-contraction coupling, elevated intracellular Ca(2+) suppresses mutant channel INaL and protects cells from delayed repolarization. PMID: 26022185
- Results show that Nav1.5 upregulation correlates with disease severity in monophasic and chronic-relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and that Nav1.5 expression in astrocytes is modulated in parallel with periods of disease and remission PMID: 25144393
- FoxO1 is involved in the modulation of NaV1.5 expression in ischemic heart disease. PMID: 24956219
- Our results suggested that the main expression subtype of sodium channels was Nav1.5 of early embryonic cardiomyocytes. PMID: 25246060
- Expression of NaV1.5 in cardiomyocytes is regulated by the PDZ domain-binding motif. PMID: 24895455
- disruption of the molecular clock in the adult heart slows heart rate, increases arrhythmias, and decreases the functional expression of Scn5a. PMID: 23364267
- AP durations were smallest in the RV of Scn5a+/-, fulfilling predictions of an increased heterogeneity of repolarization as an additional possible electrophysiological mechanism for arrhythmogenesis in BrS. PMID: 22773948
- For Brugada syndrome mutation G1743R, MOG1 restored the impaired PM expression of the mutant protein and restored I(Na) in a heterozygous state (mixture of wild type and mutant Na(v)1.5) to a full level of a homozygous wild-type state. PMID: 23420830
- The heart tissue of deoxycorticosterone acetate induced cardiomyopathic mice showed no change in SCN5A mRNA abundance or Nav1.5 protein membrane expression. PMID: 23123323
- Murine Scn5a locus was disrupted, and expression of human wild-type SCN5A cDNA substituted, identifying variable late I(Na) as a modulator of gender-dependent arrhythmia susceptibility. PMID: 22562703
- Expression of Nav1.5 participates in the generation of fibrillation potentials in denervated rat skeletal muscle. PMID: 22336133
- a TBX5-responsive enhancer downstream of Scn5a is sufficient to drive ventricular conduction system expression in vivo, dependent on canonical T-box binding sites PMID: 22728936
- Multiple pluripotent stem cell lines are generated that contain a sodium (NA)-positive channel mutation causing a cardiac Na-positive channel overlap syndrome. PMID: 22647976
- Finding sugget that Foxo1 regulates Na(V)1.5 expression by directly binding the SCN5a promoter and affecting its transcriptional activity. PMID: 22400069
- Scn5a cardiac system, in overlap with corresponding features reported in loss-of-function Na(+) channel mutations, shows compromised sinoatrial node pacemaker and conduction function PMID: 22287583
- Na(v)1.5-dependent increase in Na(+influx activates CaMKII, which in turn phosphorylates Na(v)1.5, further promoting Na(+) influx. Pharmacological inhibition of either CaMKII or Na(v)1.5 ameliorates cardiac dysfunction caused by excessive Na(+) influx. PMID: 21677263
- Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 13 regulates Na(V)1.5 sodium channels and conduction velocity in murine hearts. PMID: 21817159
- the LQTS mutation N1325S in SCN5A causes cardiac fibrosis and contractile dysfunction in mice, possibly through cellular mechanisms involving aberrant cardiomyocyte apoptosis PMID: 19762097
- genotype, age, and sex all exert independent and interacting effects on cardiac conduction with the greatest effects on ventricular activation times in the old male Scn5a +/-. PMID: 21127902
- Utrophin plays a central role in the regulation of Na(v)1.5 in dystrophin-deficient mice. PMID: 20952415
- SAP97 and dystrophin macromolecular complexes determine two pools of cardiac sodium channels Nav1.5 in cardiomyocytes. PMID: 21164104
- The right ventricular outflow tract of Scn5a+/- hearts also showed steeper restitution curves, with the diastolic interval at which the gradient equaled one strongly correlating with the diastolic interval PMID: 21097662
- Report atrial arrhythmogenic properties in wild-type and Scn5a+/- murine hearts. PMID: 20621962
- Age, sex and Scn5a genotype each exert varying effects on the observed ECG parameters. PMID: 20331542
- Aged Scn5a+/DeltaKPQ hearts exhibit an increased atrial arrhythmogenicity. PMID: 20552221
- Studies indicate that Scn5a(+/-) mice show similar phenotypic heterogeneity as SCN5A-mutated patients. PMID: 20174578
- Slowed conduction and ventricular tachycardia after targeted disruption of the cardiac sodium channel gene Scn5a PMID: 11972032
- may play a role in the physiology of the central nervous system (generation and propagation of electrical signals by axons) PMID: 12499865
- Stimulation of protein kinase c inhibits disease-linked mutant SCN5A channel bursting via phosphorylation-induced alteration of residue 1503 of the Na+ channel alpha-subunit; Sympathetic nerve activity may contribute directly to suppression of bursting PMID: 12796143
- Nav1.5 and pYbeta1 are found in ventricular myocytes and are in close association with both N-cadherin and connexin-43 PMID: 15272007
- murine Na(+) channel has both 5'- and 3'-untranslated region mRNA variants that are developmentally regulated and that the promoter region contains two distinct cardiac-specific enhancer regions PMID: 15485820
- Scn5a+/- mice convincingly recapitulate the Lenegre's disease phenotype, including progressive impairment with aging of atrial and ventricular conduction associated with myocardial rearrangements and fibrosis PMID: 15809371
- Scn5a+/- mice showed depressed heart rates and occasional sino-atrial (SA) block PMID: 15932895
- In aged heterozygous mice, reduced Scn5a expression is accompanied by the presence of reactive fibrosis and disarrangement of gap junctions, which results in profound conduction impairment. PMID: 16172272
- Deletion associated with Long QT Syndrome PMID: 16403066
- these findings suggest arrhythmic effects of reduced outward currents expected in KCNE1-/- hearts and their abolition by antagonism of inward L-type Ca2+ current PMID: 17095567
- This implies that Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) ions are involved and that [Ca2+]i inhomogeneity may be the underlying mechanisms behind non-bradycardia LQT3 arrhythmogenesis associated with mutation N(1325)S. PMID: 17118339
- VT in a genetic long QT syndrome3 model using optical mapping. Spontaneous VT was detected in TG-NS/long QT syndrome hearts PMID: 17157817
- expression level of the SCN5A gene is a determinant for the length of the P wave duration and PR interval on electrocardiograms PMID: 17300750
- a premature truncation in the C-terminal region in a single allele of the mouse SCN5A resulted in embryonic lethality PMID: 17901361
- The electrophysiology of early afterdepolarizations and transmural gradients of repolarization in arrhythmogenesis in a genetically modified mouse heart modelling human long QT syndrome are reported. PMID: 17973950
- Demonstrate that the cardiac sodium channel, Nav1.5, shows a dynamic expression pattern during mouse heart development. PMID: 18178574
- in cardiomyocytes, MOG1 is mostly localized in the cell membrane and co-localized with Nav1.5, indicating that MOG1 is a critical regulator of sodium channel function in the heart PMID: 18184654
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Cell membrane, sarcolemma, T-tubule.
-
蛋白家族:Sodium channel (TC 1.A.1.10) family, Nav1.5/SCN5A subfamily
-
組織特異性:Expressed in the myocardium.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
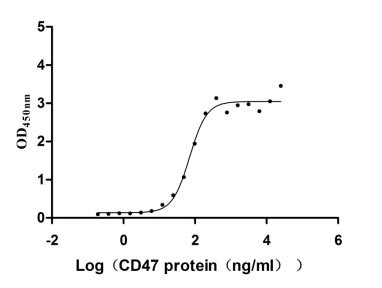
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 (TNFSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
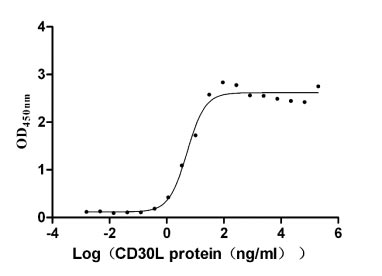
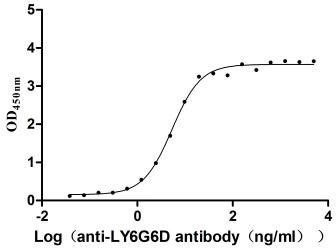
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
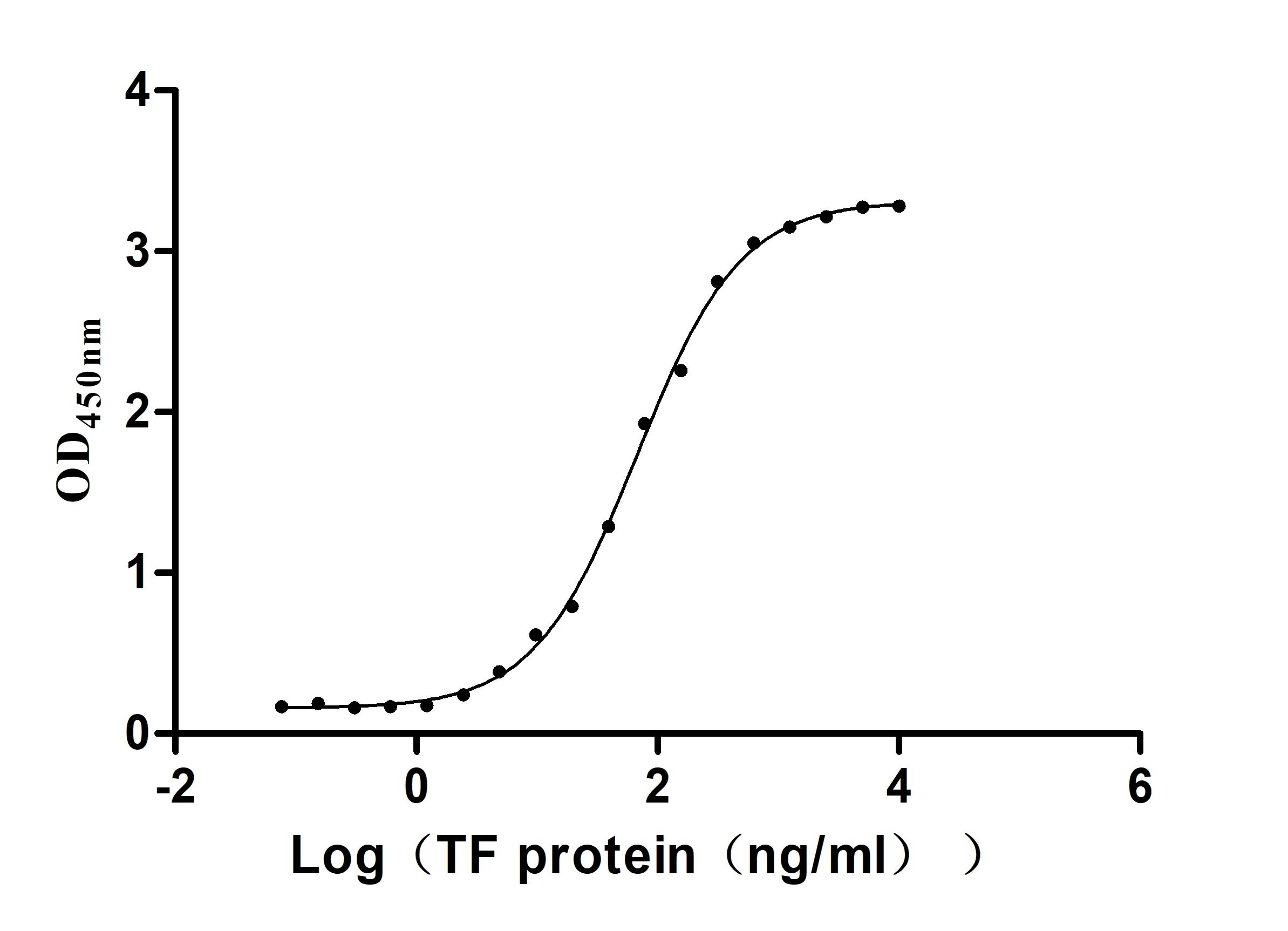
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
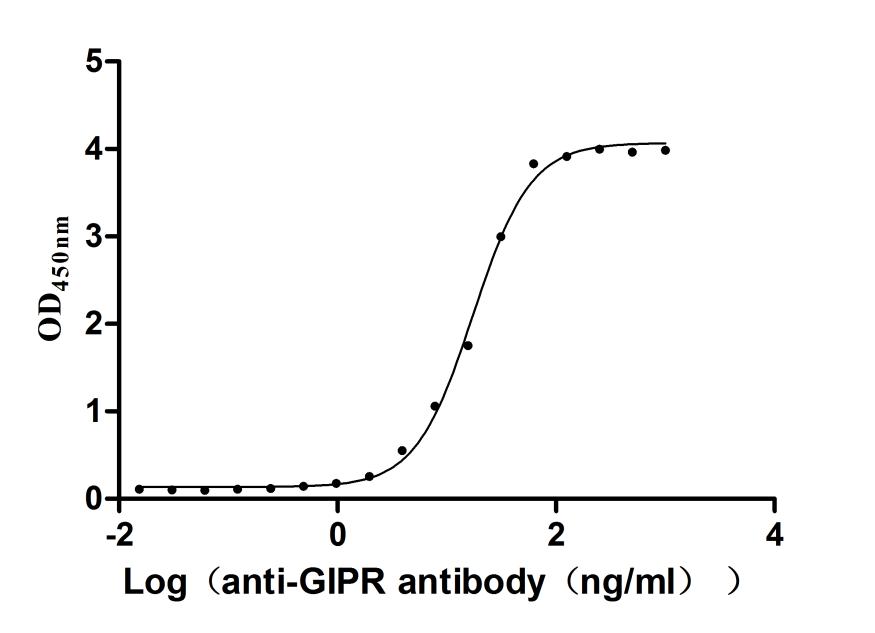
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)

-AC1.jpg)